World's first process technology for copper-internal-electrode-based capacitors for high-Speed LSIs developed
Fujitsu Laboratories today announced the development of a process technology to produce capacitors for high-speed LSI chips, which as a world's first employs copper for internal electrodes. The use of copper for internal electrodes lowers the impedance of the capacitor itself, and by mounting the capacitor directly below the LSI chip, impedance from the circuits can also be reduced, resulting in increase of current-flow efficiency by 10 times compared to previously available technology. The new technology is expected to enable the next generation of high-speed computers to operate at even higher speeds.
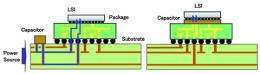
As LSI chips continue to achieve higher speeds and higher integration densities, and with many of a chip's elements all operating simultaneously, much of the current used by the chip is consumed in bursts. This can lower voltages, which may impact proper operation. In those instances in which much current is consumed, it is desirable to mount a capacitor near the LSI chip to instantly supplement the current.
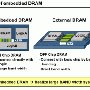
Conventionally, ceramic-chip condensers being used as power-supply capacitors have been mounted on the surface or rear of the circuit board or LSI chip package, supplying current to the LSI chip through the circuit wires. This method results in a relatively long electrical pathway between the capacitor and LSI chip, which raises impedance and would potentially create instabilities in future high-speed computers. In addition, because nickel, which has comparatively high resistance, has conventionally been used for the internal electrodes in the capacitor, the impedance of the capacitor itself has been high, limiting the speed of the power-supply current.
Fujitsu Laboratories developed a basic manufacturing method for capacitors that can provide high-speed, stable supply of current to an LSI chip.
The production of capacitors with the following key characteristics has been made possible using nano-particle deposition technology:
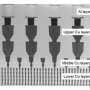
1. Internal electrodes made using low-resistance copper (a world's first)
2. Ultra-fine through-hole contact construction enabling connection directly beneath the LSI chip
3. High-reliability thin-film dielectric layer enabling high capacitance (1 µF/cm2·±ô²¹²â±ð°ù)
Employing copper for the internal electrodes to lower the impedance of the capacitor itself reduces the length of the circuits between the capacitor and the LSI chip, making it is possible to limit impedance of the power-supply line. These factors together result in a power supply that is 10 times as efficient for operationally stable high-speed LSI chips, a development that is expected to contribute to higher computer speeds.
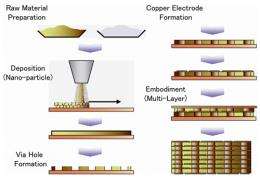
Fujitsu Laboratories will continue with development of technologies to enable miniaturization of the capacitor terminals and multi-layering, aiming to apply this new technology to computers around 2015.
Provided by Fujitsu Corporation