Renewable energy: Nanotubes to channel osmotic power
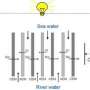
The salinity difference between fresh water and salt water could be a source of renewable energy. However, power yields from existing techniques are not high enough to make them viable. A solution to this problem may now have been found.
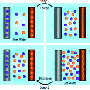
A team led by physicists at the Institut Lumière Matière in Lyon, in collaboration with the Institut Néel (CNRS), has discovered a new means of harnessing this energy: osmotic flow through boron nitride nanotubes generates huge electric currents, with 1,000 times the efficiency of any previous system.
To achieve this result, the researchers developed a highly novel experimental device that enabled them, for the first time, to study osmotic fluid transport through a single nanotube.
Their findings are published in the 28 February issue of Nature.
More information: Siria, A. et al. Giant osmotic energy conversion measured in a single transmembrane boron-nitride nanotube, Nature. 28 Feb 2013.
Journal information: Nature
Provided by CNRS