Why the central Pacific El Nino is harder to predict than eastern Pacific El Nino
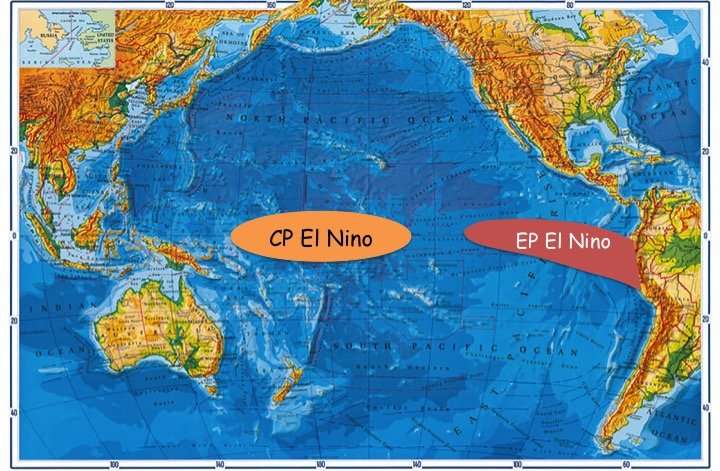
The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), which is one of the most striking interannual variabilities in the tropical Pacific, has been extensively studied for several decades. Understanding the changes in its characteristics is still an important issue in environmental and socioeconomic spheres worldwide. Recently, a new type of El Niño, the central Pacific (CP) El Niño, has emerged, in which maximum sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies are confined mostly to the CP—different to the canonical eastern Pacific (EP) El Niño, in which the maximum SST anomalies are located in the eastern Pacific. The more frequent occurrence of CP El Niño and its different impacts on global climate compared to EP El Niño have been well documented. However, a systematic examination of the performance of climate models in predicting the two types of El Niño had yet to be undertaken, and it remained controversial as to whether the predictability differs among state-of-the-art climate models.
Prof. Fei Zheng from the Institute of Atmospheric Â鶹ÒùÔºics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. Jin-Yi Yu, from the University of California, Irvine, explored the performance of the IAP's ENSO ensemble prediction system with respect to the two types of El Niño, focusing on the nine EP El Niño and twelve CP El Niño events that have occurred since 1950. "We found that the skill scores for EP events were significantly better than those for CP events at all lead times," says Zheng, "the possible reasons are related to the systematic forecast biases coming mostly from the prediction of CP events; and systematic error characterized by an overly warm eastern Pacific during the spring season, indicating a stronger spring prediction barrier for CP El Niño."
Further improvements to coupled atmosphere-ocean models in terms of CP El Niño prediction should be recognized as a key and high-priority task for the climate prediction community. The study was recently published in Advanced in Atmospheric Sciences.
More information: Fei Zheng et al, Contrasting the skills and biases of deterministic predictions for the two types of El Niño, Advances in Atmospheric Sciences (2017).
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences



















