High-refractive-index material retains high transmissivity after annealing at 850 degrees C
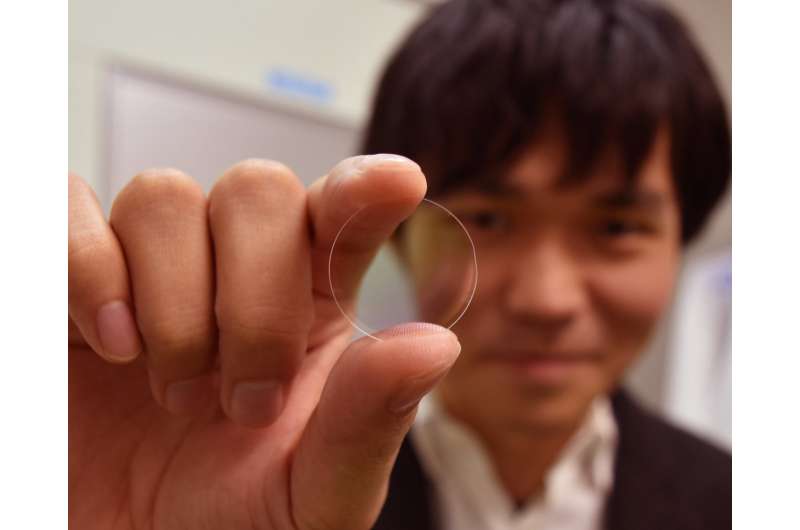
Toyohashi University of Technology researchers in collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), have developed a new material capable of retaining high transmissivity after thermal treatment at 850°C and successfully applied the material to optical devices. The researchers alternately laminated film of this high-refractive-index material and film of a low-refractive-index material to form a dielectric mirror and then used the mirror for magneto-optical device production, which requires thermal treatment at high temperatures.
Recent research has shown that combining well-known, superior materials can yield new materials that have a greatly enhanced performance compared to conventional materials. However, combining different materials often proves to be a challenge; a material with good properties when used alone can cause new problems when combined with another material. Heat-related problems are among the easiest of these problems to understand. For example, when a material that requires thermal treatment at a certain temperature is combined with another material that degrades at that temperature, the resulting product's performance is degraded, making such a combination pointless.
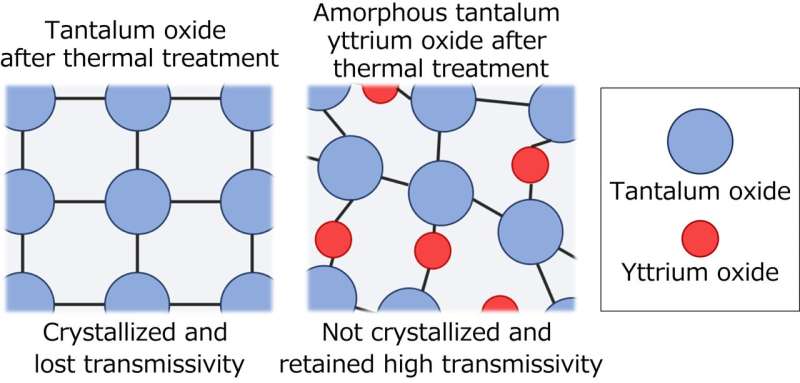
In this study, the research group of Toyohashi University of Technology in collaboration with Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) alternately laminated a high-refractive-index material and a low-refractive-index material to form a dielectric mirror and combined it with transparent magnetic garnet. The magnetic garnet requires thermal treatment at about 750°C during formation, and therefore the dielectric mirror needs to withstand this temperature. It is well known that tantalum oxide3, which is widely used as a high-refractive-index material in dielectric mirrors, crystallizes and loses much of its transmissivity at about 700°C.
This study uses amorphous tantalum yttrium oxide, which has been studied for use as an insulate material, as a high-refractive-index material. Amorphous tantalum yttrium oxide is formed by adding a trace amount of yttrium oxide to tantalum oxide, and retains transmissivity after thermal treatment at 850°C, making it suitable for combination with magnetic garnet. With this discovery, the research group overcame the problem of performance degradation caused by thermal treatment, and succeeded in enhancing the performance of an integrated device composed of a dielectric mirror and magnetic garnet by about ten times.
"We used amorphous tantalum yttrium oxide to form a dielectric mirror and combined it with magnetic garnet. Actually, other than magnetic garnet, there are more materials that have not been combined with dielectric mirrors because of the high-temperature thermal treatment that is required. I hope that our findings will help make such materials usable too," says Assistant Professor Taichi Goto.
The amorphous tantalum yttrium oxide contains tantalum oxide as its major constituent and about 14 percent yttrium oxide. The presence of yttrium oxide molecules between tantalum oxide molecules prevents crystallization, resulting in an increase in the crystallization temperature to about 850°C or higher. Tantalum oxide loses its transmissivity when crystallized, but in the study the crystallization temperature was increased and thus the loss of transmissivity of tantalum oxide was successfully prevented. The study provides a new material that is capable of giving enhanced performance to optical devices.
"Magnetic garnet has a wide range of applications, such as ultra-fast displays, spin wave devices, and lasers. Performance of these devices can be greatly enhanced by combining magnetic garnet with dielectric mirrors containing our high-refractive-index material," says Takuya Yoshimoto, a Ph.D. student in charge of sample preparation for the study.
The new material amorphous tantalum yttrium oxide is producible and stable at room temperature, and is promising for future application to spin wave devices, compact laser devices containing magnetic garnet, and so on.
More information: Takuya Yoshimoto et al, Thermally stable amorphous tantalum yttrium oxide with low IR absorption for magnetophotonic devices, Scientific Reports (2017).
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by Toyohashi University of Technology