September 24, 2018 report
Material made from single molecule self-forms into a lattice that can self-heal, store gases

Bob Yirka
news contributor
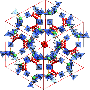
![Modes of C鈥揌路路路N bonds in Pyopen鈯僊eCN and crystal-packing diagrams of Pyopen鈯僊eCN. (A) Drawings representing the modes of C鈥揌路路路N bonds in Pyopen鈯僊eCN. (B to E) CPK representations of the crystal-packing diagrams of Pyopen鈯僊eCN. Orange outlines indicate the C鈥揌路路路N-bonded roofs and floors in Pyopen鈯僊eCN [(B) and (C)], and dashed purple outlines indicate the wall connected to the roof and floor [(B), (C), and (E)]. Credit: (c) Science (2018). DOI: 10.1126/science.aat6394 **Material made from just a single molecule that self-forms into a lattice that can self-heal and store gases](https://scx1.b-cdn.net/csz/news/800a/2018/5ba8ce8281fe4.jpg)
A team of researchers affiliated with several institutions in Japan has developed a material made from just a single molecule that self-forms into a lattice that can self-heal and store gases. In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes synthesizing the aromatic molecule, which bears a symmetrical outer shell.
The researchers note that most porous materials are made from linkers and connecting units鈥攎etal organic frameworks are one example. Such frameworks are often custom-developed to allow for storing other material, such as hydrogen, in the pores. The downside to such an approach is the multitude of options available, which requires researchers to spend time screening for the optimal structure. In this new effort, the researchers report on the development of a new porous material made from a single synthesized molecule. They claim it is possible to create a complex, useful type of material without a complex set of building blocks.
The molecule the team made had a symmetrical outer shell, giving it a shape akin to a propeller. It consisted of three polar dipyridylphenyl parts hooked to a middle non-polar mesitylene. In the presence of isopropanol or acetonitrile, it assembled automatically into a network that was held together by hydrogen bonds (non-classical). The researchers note that the bonds were weaker than normal hydrogen bonds but were stable up to 202掳C. They further note that other similar-purpose crystals begin to degrade at temperatures of 130掳C. Above the stable point, the pores in the crystal started to collapse causing the material to become non-porous鈥攕uggesting a means for delivering a material that it has been holding. Interestingly, the researchers found that the pores could be regenerated by cooling the material and treating it with acetonitrile vapor鈥攁 form of self-healing.
The researchers note that the oddly shaped molecule serves as a linker and connector allowing for the creation of a simple porous network in a material. They note also that the arms of the propeller serve different functions鈥攆rom walls, to roof to floor鈥攁ll around 6脜 wide pores that offer a size capable of harboring nitrogen gas or solvents.
Written for you by our author 鈥攖his article is the result of careful human work. We rely on readers like you to keep independent science journalism alive. If this reporting matters to you, please consider a (especially monthly). You'll get an ad-free account as a thank-you.
More information: Hiroshi Yamagishi et al. Self-assembly of lattices with high structural complexity from a geometrically simple molecule, Science (2018).
Journal information: Science
漏 2018 麻豆淫院