The gold nanoparticles embedded in silicate bioactive glasses prepared by the sol-gel method. Image credit: Materials Science and Engineering: C, Credit: Biomedical Materials, doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-605X/aafd7d
Healing is a in adult skin impairments, requiring collaborative biochemical processes for onsite repair. Diverse cell types (macrophages, leukocytes, mast cells) contribute to the associated phases of proliferation, migration, matrix synthesis and contraction, coupled with growth factors and matrix signals at the site of the wound. Understanding signal control and cellular activity at the site could help explain the process of adult skin repair beyond mere patching up and more as regeneration, to assess biomechanics and implement strategies for accelerated wound repair in regenerative medicine.
Bioengineers, materials scientists and life scientists who study the intersection of have developed , and for partial and full wound healing. Limitations of these procedures can delay the and is a significant clinical problem in healthcare, due to the potential risk of and disease transmission. Tissue engineering strategies for skin regeneration is a practical approach involving the use of bioactive biomaterials for and faster revascularization.
In a recent study, Sorin Marza and co-workers at the interdisciplinary research institutes and faculties of physics, bio-nano-sciences, pharmacy and medicine, developed bioactive glass-gold nanoparticles (BG-AuNPs) to promote the growth of and induce wound healing. In the study, the scientists investigated the impact of BG-AuNP composites as a topical ointment for 14 days on skin wound healing using an experimental rat model. Marza et al. developed a sol-gel of BGs and BG-AuNP composites mixed with Vaseline at concentrations of 6,12 and 18 weight percent (wt%) to understand the repair response of the skin. The scientists observed granulomatous reactions during the process of healing in the wounds treated with the BG-Vaseline ointment. The results are now published in Biomedical Materials, IOP Publishing.
Angiogenesis, or the formation of new blood vessels from existing vessels is an important process during skin regeneration. Bioactive glass is responsible for local cellular responses due to , stimulating the release of growth factors such as VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) and bFGF (basic fibroblast growth factor) to cause an angiogenic effect. A variety of studies on tissue engineering have demonstrated the in wound healing, based on results in animal models in vivo. In its principle of action, scientists have reported that bioactive glass stimulated the process by to enhance the paracrine effect between macrophages and repairing cells.
(AuNPs) are similarly becoming important in medicine due to their of biocompatibility, surface modification, stability and optical properties. Despite their challenging approaches, a can stimulate cell proliferation during wound repair. by the same research team showed that bioactive glass with AuNPs could stimulate the proliferation of human keratinocyte cells (HaCaT), which constitute 95 percent to 97 percent of the epidermis on the skin surface. In the present study, Marza et al. investigated the potential of dermal tissue regeneration in vivo. By day 14, they observed that both BG and BG-AuNP-Vaseline ointments could stimulate complete skin regeneration in experimental rat models, substantiated with gold standard histopathological analyses.
Marza et al. freshly prepared spherical AuNPs ranging from sizes of 15 nm to 30 nm, confirmed using (TEM) micrographs to embed within the glass matrix. Using (XRD) patterns of the glass samples, the scientists investigated the amorphous structures to identify the crystallization centers and the gold signature. The characterization studies for the composite samples also included (FTIR), which provided spectra typical for a . To develop the glass composition ointment, the scientists dispersed the powder composite materials in Vaseline. They then used (DLS) to measure particle size distributions and corroborate the difference in sizes between the BG-Vaseline and BG-AuNP-Vaseline sample structures.
After extensive materials characterization, the scientists conducted biofunctionalization studies in vitro with keratinocytes cell cultures to verify biocompatibility prior to conducting surgical procedures in a translational animal model. As before, Marza et al. investigated the proliferation of and obtained comparable results of good in vitro tolerance during keratinocytes proliferation on both materials (BG and BG-AuNPs). The outcomes substantiated the composites for use as ointments for in vivo investigations.
To assess the healing potential of BG and BG-AuNPs in the Vaseline ointments, Mayer et al. formed composites of 6, 12 and 18 weight percent concentration. For comparison, the scientists used Vaseline as a positive control. In the rat models, the scientists carefully created four skin excision wounds by successfully replicating a . They used a specific method on each rat when applying the ointment; (1) the upper left excision was kept as the control without ointment, (2) on the left lower excision, the scientists applied the BG-Vaseline ointment, (3) on the upper right excision, they applied Vaseline alone and (4) on the lower right excision, they applied the BG-AuNP-Vaseline ointment.
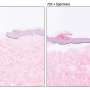
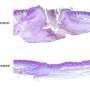
The scientists used 30 rats in the study with 10 rats assigned to separate groups (6% BG-Vaseline and BG-AuNPs-Vaseline ointment; 12% BG/BG-AuNPs-Vaseline; 18% BG/BG-AuNPs-Vaseline). The working protocol was the same for each group. After ointment application, the scientists added sterile bandages to the wound sites on rats to prevent wound infection postoperatively and administered Tramadol subcutaneously as an analgesic. By day 13, the wounds were closed in all animals. After 14 days, they humanely euthanized the animals and conducted histological examinations to reveal mild inflammatory reactions and wound healing responses in the respective animal groups. In all groups, vascular proliferation was mild to moderate.
Mayer et al. specifically observed largely complete healing with intact epidermis, dermis and skin appendages in the 18 percent BG-AuNPs-Vaseline group. They also observed a lack of vascular proliferation for this group, which they attributed to advanced healing and late vascular remodeling. In this way, Mayer et al. extensively characterized and established bioactive glass-gold nanoparticle based Vaseline ointments as promising materials for wound healing. The research team will conduct further studies to optimize the wound healing ointment for investigations in bench to bedside translation.
Written for you by our author —this article is the result of careful human work. We rely on readers like you to keep independent science journalism alive. If this reporting matters to you, please consider a (especially monthly). You'll get an ad-free account as a thank-you.
More information: S M Mârza et al. Skin wound regeneration with bioactive glass-gold nanoparticles ointment, Biomedical Materials (2019).
K. Magyari et al. Novel bioactive glass-AuNP composites for biomedical applications, Materials Science and Engineering: C (2017).
Xusheng Wang et al. The mouse excisional wound splinting model, including applications for stem cell transplantation, Nature Protocols (2013).
A.C. Jayalekshmi et al. Gold nanoparticle incorporated polymer/bioactive glass composite for controlled drug delivery application, Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces (2014).
Wound healing—aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science. 1997 Apr 4;276(5309):75-81.
Journal information: Nature Protocols , Science
© 2019 Science X Network