February 9, 2021 report
Retesting of ancient teeth found in China shows they are 16,000 years old鈥攏ot 120,000

Bob Yirka
news contributor

A team of researchers affiliated with a host of institutions in China, along with one from Australia, one from Taiwan and one from the U.S., has found evidence that contradicts the finding of a prior effort that reported ancient human teeth found at a dig site in China were 120,000 years old. In their paper published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the group describes how they tested the teeth and what they found.
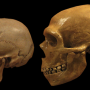
Most archeologists agree that modern humans evolved approximately 500,000 to 315,000 years ago, and they migrated out of Africa approximately 65,000 to 45,000 years ago into parts of Eurasia鈥攐ther non-modern-human hominins made the trek much earlier, but all went extinct. This timeline was called into question back in 2015 when a team of archeologists found fossilized teeth in five caves in a southern part of China, and claimed they were approximately 120,000 years old. In this new effort, the researchers have reexamined the teeth and have found the original researchers were in error鈥攖heir testing showed the teeth are just 16,000 years old.
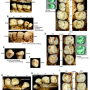
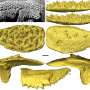
In looking at the methods used to date the teeth by the original team, the researchers found that most of the work had involved testing materials such as sediment and capping flowstones found in the vicinity of the teeth. The teeth themselves had not been tested. In the new effort, the researchers found small bits of mitochondrial DNA in some of the teeth (and some nearby charcoal) and tested them using carbon-14 dating. Their results showed the teeth belonged to modern humans living in the area during the Holocene. The researchers also found that the DNA from one of the tested samples matched people living in modern Tibet and Burma. They conclude that the teeth did not come from modern humans 120,000 years ago, and thus, the theory that modern humans migrated to Eurasia 65,000 to 45,000 years ago still stands. They also suggest that other researchers carrying out similar research efforts always directly test samples they find using carbon-14 dating to ensure accuracy.
Written for you by our author 鈥攖his article is the result of careful human work. We rely on readers like you to keep independent science journalism alive. If this reporting matters to you, please consider a (especially monthly). You'll get an ad-free account as a thank-you.
More information: Xue-feng Sun et al. Ancient DNA and multimethod dating confirm the late arrival of anatomically modern humans in southern China, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2021).
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Provided by Science X Network
漏 2021 Science X Network