Direct synthesis of isoparaffin-rich gasoline from syngas
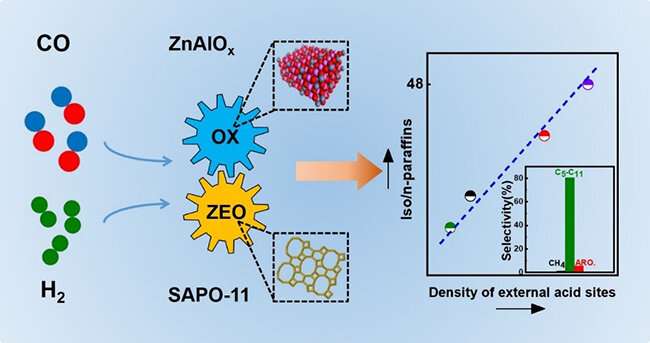
A research team led by Prof. Pan Xiulian and Prof. Bao Xinhe from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Â鶹ÒùÔºics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences realized the direct synthesis of isoparaffin-rich gasoline from syngas using ZnAlOx-SAPO-11 oxide-zeolite (OXZEO) catalysts.
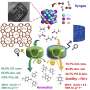
They elucidated the active sites of isoparaffin formation, which provided guidance for the one-step synthesis of high-quality gasoline from syngas.
This study was published in ACS Energy Letters on March 23.
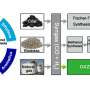
Previously, the DICP team proposed a new catalyst concept based on metal oxide-zeolite (OXZEO) bi-functional catalysts, and it enabled the direct conversion of syngas to a variety of chemicals and fuels with high selectivity, such as light olefins, ethylene, gasoline, aromatics and oxygenates. The OXZEO concept provided a new technology platform for the highly efficient utilization of coal and other carbon resources.
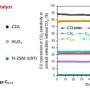
In this study, they achieved 34% CO conversion and 82% gasoline selectivity by modulating the acid sites distribution of zeolite, in which the iso/n-paraffins ratio was as high as 38. By optimizing the reaction conditions, they increased the ratio of iso/n-paraffins as high as 48, which was the highest value of the iso/n-paraffins ratio reported so far.
Moreover, a 150-hour on stream test of the catalyst indicated rather stable activity in syngas-to-gasoline.
Further studies showed that the external acid sites of the zeolite could be the active sites for the formation of branched, especially the multi-branched isoparaffins.
"This study provided important guidance for the one-step synthesis of high-quality gasoline from syngas and even CO2," said Prof. Pan.
More information: Jingyao Feng et al, Direct Synthesis of Isoparaffin-rich Gasoline from Syngas, ACS Energy Letters (2022).
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences