Collisions with electrons cool molecular ions

A lone molecule free in cold space will cool by slowing down its rotation鈥攊t will spontaneously lose its rotational energy in quantum transitions, typically only once in many seconds. This process can be accelerated, slowed down, or even inverted by collisions with surrounding particles.
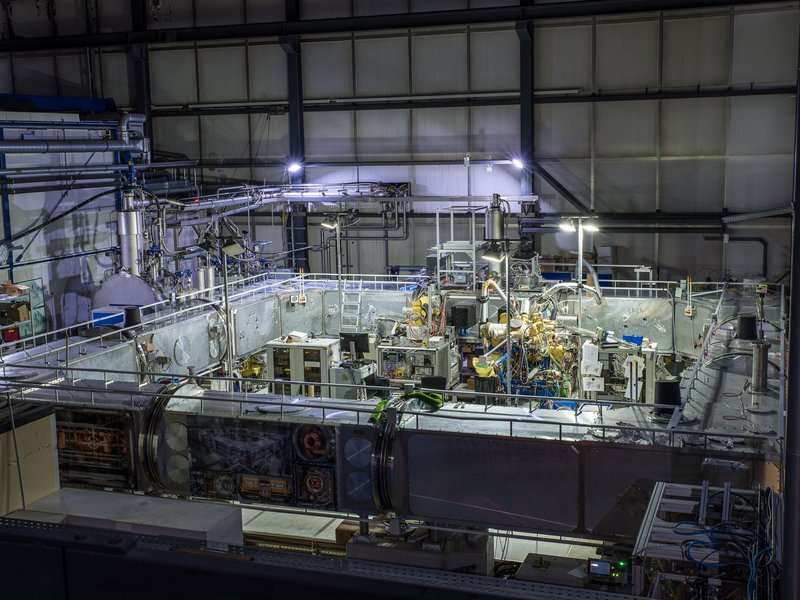
In an experiment at the ultracold storage ring CSR, researchers of the MPI for Nuclear 麻豆淫院ics measured the rate of quantum transitions due to encounters between molecules and electrons by bringing isolated, charged molecules in contact with electrons under controlled conditions at about 26 Kelvin. Thus, they could make this rate鈥攐nly known by complex calculations so far鈥攈igh enough to be quantitatively determined in an experiment at last.
The researchers probed the occupation of quantum energy levels in methylidene ions (CH+) by laser spectroscopy during up to 10 minutes of storage. As the spontaneous quantum transitions generate electromagnetic radiation, they are connected to black-body excitation of the molecules as well. Thus, the electrons compete with the ubiquitous radiative interactions to determine the occupation of rotational quantum levels in cold molecules. Therefore, electron-induced rates of quantum-level changes are crucial in analyzing the faint signals of molecules in space detected by radio telescopes, or in predicting level-dependent chemical reactivity in dilute, cold plasmas. The research is published in 麻豆淫院ical Review Letters.
More information: 脕bel K谩losi et al, Laser Probing of the Rotational Cooling of Molecular Ions by Electron Collisions, 麻豆淫院ical Review Letters (2022).
Journal information: 麻豆淫院ical Review Letters
Provided by Max Planck Society