Stab-resistant fabric gains strength from carbon nanotubes, polyacrylate
Fabrics that resist knife cuts can help prevent injuries and save lives. But a sharp enough knife or a very forceful jab can get through some of these materials. Now, researchers report in ACS Applied Nano Materials that carbon nanotubes and polyacrylate strengthen conventional aramid to produce lightweight, soft fabrics that provide better protection. Applications include anti-stabbing clothing, helmets and insoles, as well as cut-resistant packaging.
Soft body armor is typically made from aramid, ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene, or carbon and glass fabrics. Their puncture resistance depends, in part, on the friction between yarn fibers within these materials. Up to a point, greater friction means greater protection. Manufacturers can boost friction by roughening the fiber surfaces, but that requires a complicated process, and product yield is low.
Alternatively, the bonding force between yarns can be enhanced by adding another component, such as a sheer thickening fluid (STF) or a polyurethane (PU) coating. But these composite fabrics can't simultaneously satisfy the requirements for thinness, flexibility and light weight. Ting-Ting Li, Xing-xiang Zhang and colleagues wanted to find another way to improve performance while satisfying these criteria.
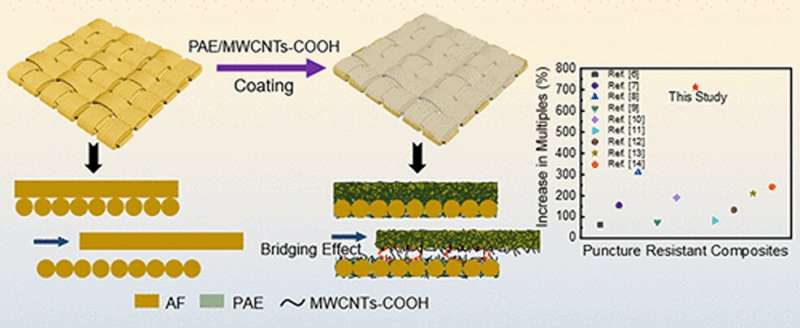
The researchers tested a polyacrylate emulsion (PAE), STF and PU as coatings on aramid fabric. In simulated stabbing tests, aramid fabric coated with PAE outperformed the uncoated material used by itself or in combination with STF or PU.
Carbon nanotubes are known to make composites tougher, and adding them to aramid/PAE further improved impact resistance. The team says that's because the nanotubes created bridges between the fibers, thereby increasing friction. The nanotubes also formed a thin, protective network that dispersed stress away from the point of impact and helped prevent fiber disintegration. The new lightweight, flexible, puncture-resistant composite fabric could be useful in military and civilian applications, according to the researchers.
More information: Wen-hua Cai et al, Polyacrylate and Carboxylic Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Strengthened Aramid Fabrics as Flexible Puncture-Resistant Composites for Anti-Stabbing Applications, ACS Applied Nano Materials (2023).
Provided by American Chemical Society