N-17 is a potential inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein, shows nanomolar activity against the HCoV-OC43 and SARS-CoV-2 viruses and may prevent SARS-CoV-2 replication and transcription by blocking the packaging process of viral RNA. Credit: Acta Materia Medica (2023). DOI: 10.15212/AMM-2023-0021
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has spread globally since 2020. The nucleocapsid (N) protein plays a crucial role in the life cycle of SARS-CoV-2.
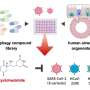
The authors of an article published in Acta Materia Medica have established a method to screen inhibitors of N protein by using microscale thermophoresis assays to obtain potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents. 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4,6-heptatrien-3-one (N-17, a diphenylheptane) was identified as a compound with outstanding inhibitory activity.
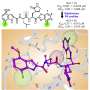
The binding of N-17 to the N-terminal domain of N protein (N-NTD) was further validated by using drug affinity responsive target stability assays. The ability of N-17 to bind N protein was evaluated and the affinity of N-17 to the N-NTD with molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation was predicted.
N-17 exhibited excellent anti-viral activity against HCoV-OC43 and SARS-CoV-2, with EC50 values of 0.16 ± 0.01 μM and 0.17 ± 0.07 μM, respectively. Thus, a novel SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor targeting the N protein was discovered and its anti-viral activity in vitro was validated. The results may contribute to the development of promising therapeutic agents for COVID-19
More information: Yang Liu et al, 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4,6-heptatrien-3-one inhibits SARS-CoV-2 by targeting the nucleocapsid protein, Acta Materia Medica (2023).
Provided by Compuscript Ltd