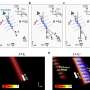
No longer ships passing in the night: These electromagnetic waves had head-on collisions

A research team at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) has shown that it is possible to manipulate photons so that they can collide, interacting in new ways as they cross paths. The discovery, detailed in Nature Â鶹ÒùÔºics, will allow scientists who develop technologies rooted in electromagnetic wave propagation to make significant advances in telecommunications, optical computing and energy applications.
The breakthrough took place in the lab of Andrea Alù, Distinguished Professor and Einstein Professor of Â鶹ÒùÔºics at The City University of New York Graduate Center and founding director of the CUNY ASRC Photonics Initiative. It was facilitated by another recent experiment demonstrating time-reflections for electromagnetic waves.
"Our work is building on a series of experiments that show how we can create metamaterials with unique properties that emerge from abrupt time variations of their electromagnetic properties. These variations allow us to manipulate wave propagation in ways not seen in nature," said Alù.
"This newest work shows that we can use abrupt temporal changes in tailored metamaterials—known as time interfaces—to make waves collide as if they were massive objects. We were also able to control whether the waves exchanged, gained or lost energy during these collisions."
Typically, when two electromagnetic waves cross paths, they move right through each other without interacting. This is very different from what happens when two massive objects, like two balls, bump into each other. In the latter case, the particles collide, and their mechanical features determine whether the energy is conserved, lost or increased in the collision. For example, when two billiard balls collide, the total energy in the system is conserved, while when two rubber balls collide, they typically lose energy in the collision.
While photons would be expected to go through each other without any interaction, by triggering a time interface the scientists were able to demonstrate strong photon-photon interactions and control the nature of the collision.
The research team's work was inspired by speculation about whether it would be possible to erase an unwanted mechanical wave, such as a tsunami or a seismic wave, by throwing another similar wave against it to counter it. "While such an outcome is impossible in conventional wave physics, we knew it was possible in principle with a temporal metamaterial," said Emanuele Galiffi, a postdoctoral fellow with Alù's lab and the study's leading author. "Our experiment allowed us to demonstrate this concept in action for electromagnetic waves."
The scientists also proposed and demonstrated an application of their concept to shape electromagnetic pulses by colliding them against each other. "This technique allows us to use an additional signal as a mold to sculpt a pulse that we are interested in structuring," said Gengyu Xu, a postdoctoral fellow with Alù's lab and co-leading author of the paper. "We have shown this for radio frequencies, and we are now working to realize this sculpting ability at higher frequencies."
The team's work developing methods to dictate how propagating electromagnetic waves interact and shape each other could benefit wireless communications, imaging, computing and energy harvesting technologies, among other advances.
More information: Broadband coherent wave control through photonic collisions at time interfaces, Nature Â鶹ÒùÔºics (2023). ,
Journal information: Nature Â鶹ÒùÔºics
Provided by CUNY Advanced Science Research Center