Magnetic nanocatalysts enhance tumor treatment via electronic density regulation

Cancer therapy has always struggled with targeting tumor cells effectively while minimizing damage to healthy tissue. Traditional treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation, often lack precision and cause serious side effects. As a result, there is a growing interest in advanced nanomaterials with enhanced catalytic and therapeutic properties, such as nanocatalysts, which can improve cancer treatment through methods like chemical dynamic therapy (CDT) and photothermal therapy (PTT).
A research team led by Profs. Wang Hui and Zhang Xin from the Hefei Institutes of 麻豆淫院ical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a novel carbon-coated nickel ferrite (NFN@C) nanocatalyst with significant potential in cancer therapy.
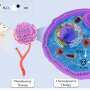
In their study, in Advanced Functional Materials, the researchers introduced nickel to the nanocatalyst, which changes its electronic structure and improves its catalytic properties. This enhancement helps the nanocatalyst convert hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into hydroxyl radicals (路OH) in the tumor environment, making CDT more effective.
Using electron paramagnetic resonance technology, the team saw a noticeable increase in the 路OH signal, indicating that nickel boosts the efficiency of the Fenton reaction.
Additionally, NFN@C excels at converting near-infrared (NIR-II) light into heat, enabling a synergistic effect between PTT and CDT that further enhances its potential in fighting cancer.
Theoretical calculations also revealed that the addition of nickel lowers the activation energy for the Fenton reaction, improving its efficiency and selectivity. These insights could help optimize similar nanomaterials for other uses.
In experiments, NFN@C showed strong anticancer effects in lab tests and successfully reduced tumors in animal models. When exposed to NIR-II light, NFN@C significantly increased tumor cell death, demonstrating its powerful therapeutic effect. This enhanced catalytic activity could overcome the limitations of traditional treatments, offering a promising new approach to cancer therapy.
This research provides valuable insights into the design and optimization of nanocatalysts, particularly through innovative regulation of the nanocatalysts' electronic structures. "It holds promising implications for other cancer therapies and precision medicine," said Dr. Zhao Jiaping, a member of the team.
More information: Jiaping Zhao et al, Electron Density Modulation鈥怑nhanced Magnetic Nanocatalysis for Anti鈥怲umor Therapy, Advanced Functional Materials (2025).
Journal information: Advanced Functional Materials
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences