Branch development in petunia is regulated by the gene PhSLB1

A recent study has identified PhSLB1 as a crucial regulator of branch development in petunia (Petunia hybrida), offering valuable insights into plant growth mechanisms that could inform horticultural practices and crop improvement strategies.
The work in J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci..
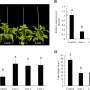
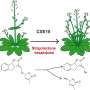
Branching is a fundamental aspect of plant architecture, directly impacting biomass production, flowering, and overall yield. The study focused on the role of PhSLB1, a gene implicated in the regulation of shoot branching, and its influence on the growth and development of petunia plants.
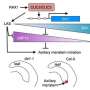
Plant architecture, including traits like height, branch number, and branch angle, is a critical agronomic characteristic in horticultural crops. The number of branches significantly influences the ornamental value of plants, affecting consumer preferences. Branching occurs when meristem tissue at the leaf axil develops into axillary buds, which can grow into lateral branches. This process is regulated by a combination of genetic factors, environmental conditions, and endogenous hormones.
Through detailed molecular and genetic analyses, researchers demonstrated that PhSLB1 plays a pivotal role in modulating branch formation. This regulation is achieved by its interaction with key signaling pathways that control the initiation and outgrowth of lateral branches. Understanding these mechanisms provides a deeper understanding of how plants adapt their architecture in response to environmental and developmental cues.
The findings have significant implications for the horticulture and agriculture industries. By manipulating the activity of PhSLB1 or its associated pathways, growers may be able to optimize plant structure for enhanced aesthetic appeal, resource efficiency, or productivity.
This research adds to the growing body of knowledge of plant developmental biology, with potential applications extending to a wide variety of ornamental and agricultural crops.
More information: Jichu Deng et al, PhSLB1 Regulates Branch Development in Petunia, J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. (2024).
Provided by American Society for Horticultural Science