Enzymes from fungi can be used to extract plant components for biofuels and bioplastics

Sadie Harley
scientific editor

Robert Egan
associate editor

Plant cell wall components such as cellulose are abundant sources of carbohydrates that are widely used in biofuels and bioproducts; however, extraction of these components from plant biomass is relatively difficult due to their complexity.
In research appearing in , investigators have found that a combination of fungal enzymes can efficiently degrade plant biomass to allow for extraction.
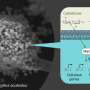
The enzymes are called cellobiose dehydrogenase (CDH) and lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase (LPMO). LPMO and CDH operate together to enhance the degradation of plant biomass as CDH can support the activity of LPMOs by activating certain cellular reactions. Recently, a new CDH enzyme was characterized from Fusarium solani, a highly adaptable fungus that can infect numerous crops.
"We found that this particular CDH enzyme worked especially well with LMPO for producing carbohydrates from plants, making it a promising candidate for biotechnology approaches to use non-edible plant biomass of diverse origin and complexity," said corresponding author Roland Ludwig, Ph.D., of BOKU University, in Austria.
More information: Interaction of class III cellobiose dehydrogenase with lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase, FEBS Open Bio (2025).
Provided by Wiley