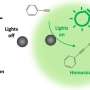
Laser-engineered platinum colloidosomes enable efficient near-infrared catalysis and cancer therapy

Lisa Lock
scientific editor

Robert Egan
associate editor

Researchers have developed a novel laser-assisted synthesis method to fabricate platinum (Pt) colloidosomes (Cs) with promising applications in near-infrared (NIR) photocatalytic and enzyme-mimicking cancer therapy.
Interband and intraband electronic excitations in transition metal nanocatalysts are crucial for generating hot carriers. Unlike well-known gold (Au), silver (Ag), and copper (Cu) nanoparticles (NPs), which directly form hot carriers by absorbing visible light, Pt NPs have limited hot carrier photogeneration ability.
However, Pt's unique d-band structure allows for a high density of electronic states near the Fermi energy. Therefore, it should exhibit photoenhanced catalysis. Leveraging this property, researchers designed sub-100-nm colloidosomes constructed from ultrasmall Pt NPs (≤5 nm) with broadband light absorption spanning from the visible to NIR wavelengths.
Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) simulations guided the structural design. A critical innovation was the use of laser-generated Mn₃O₄ nanoparticles, rich in grain boundaries, as robust scaffolds for the uniform anchoring of the ultrasmall Pt NPs. This architecture facilitated efficient generation of hot electrons even under low-energy NIR irradiation.
This study demonstrates that NIR photoexcitation of Pt Cs greatly improves the dual-enzyme (CAT and OXD) and self-cascade catalytic activities of Pt Cs. The results are in Angewandte Chemie International Edition. The research team was led by Prof. Liang Changhao from the Hefei Institutes of Â鶹ÒùÔºical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with researchers from the University of Padova of Italy and Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
Additionally, in vivo experiments demonstrate the superior antitumor ability of Pt Cs for NIR-responsive photocatalytic tumor therapy, as well as the possibility of tracking their biodistribution with the assistance of MRI guidance.
These results highlight the advantages brought by the Pt Cs successfully designed for optimal and efficient generation of hot electrons under NIR light excitation.
More information: Sihan Ji et al, Pt Colloidosomes with Broadband Absorption for Near-Infrared Light Photocatalysis through d-Band Hot-Carriers Generation, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2025).
Journal information: Angewandte Chemie International Edition
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences