Adjustable microchannel height boosts sensitivity in impedance flow cytometry

Sadie Harley
scientific editor

Robert Egan
associate editor

Many advances in medicine and drug development were possible owing to flow cytometry, a single-cell analysis technique that analyzes cells using the emitted fluorescence of their chemical tags while passing through a laser beam. Most flow cytometers possess a microfluidic channel, a small channel that regulates the flow of fluorescently tagged analytes. Flow cytometry enables quick single-cell counting and analysis, making it a cornerstone of modern biomedical research.
A powerful variant, impedance flow cytometry, replaces lasers with electrodes that detect changes in electrical impedance (the total resistance of electrical equipment to alternating current) as cells or particles pass through the microfluidic channel. This approach avoids the need for fluorescent tags, which are often costly and labor-intensive.
Despite its advantages, impedance flow cytometry suffers from low sensitivity and inconsistent readouts, since the distance between the flowing cells and electrodes varies depending on the channel height and particle size.
To fill this gap, a research team led by Associate Professor Yalikun Yaxiaer from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST), Japan, developed an innovative low-cost platform to overcome these limitations.
Their paper, in the journal Lab on a Chip, was co-authored by Mr. Trisna Julian, Dr. Naomi Tanga, Professor Yoichiroh Hosokawa from NAIST, and others.
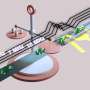
The team's design goal was straightforward; they aimed to dynamically adjust the channel height depending on particle size. They realized this by attaching a metal probe to the vertical axis of an XYZ stage—a laboratory device that enables highly precise movements in three dimensions.
By controlling the vertical position of the probe, they used its thin tip to press against the top of the 30-micrometer-high microfluidic channel of the flow cytometer. This compression squeezed the channel slightly, altering its height on demand.
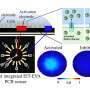
Through experiments and simulations, the team showed that enabling the flowing particles to travel closer to the sensing electrodes by reducing the channel's height led to a remarkable increase in the platform's sensitivity and accuracy.
They achieved a three-fold amplification of the impedance signal by reducing the channel height by one-third, while also reducing the signal variability to half, allowing them to easily distinguish between multiple cells of different sizes.
Notably, by introducing a camera and an object-detection algorithm, the researchers found a way to leverage clogging (unwanted deposition of particles that prevents further passage of analytes) as a strategy to optimize the platform's performance.
"Our system deliberately induces a critical constriction by deforming the channel to maximize sensitivity. However, this deformation can be released just before actual clogging occurs," explains Dr. Yaxiaer. "Thus, our approach acts like a smart microchannel that harnesses and controls the clogging phenomena."
Overall, this study establishes a much-needed foundation for the standardization of adaptive impedance flow cytometry, paving the way for its integration into clinical and research contexts where precise cell analyses are required.
"Our findings underscore the potential for a universal, high-performance impedance flow cytometry platform—one that is simple, clog-resistant, and adaptable for a wide range of biomedical applications," concludes Dr. Yaxiaer.
Collaborating with medical institutions could transform this innovative platform into a diagnostic device for point-of-care testing, and could also be leveraged for drug development and testing.
More information: Trisna Julian et al, A long-term universal impedance flow cytometry platform empowered by adaptive channel height and real-time clogging-release strategy, Lab on a Chip (2025).
Journal information: Lab on a Chip
Provided by Nara Institute of Science and Technology