Quantum dot and polymer cross-linking enables 50% stretch capability for micro-LED displays

Gaby Clark
scientific editor

Robert Egan
associate editor

A research team has developed a next-generation display core material with excellent stretchability and superior color reproduction. The team developed a high-performance color-conversion layer that is more flexible and vivid than conventional ones. This layer was successfully applied to the development of a stretchable micro-LED display, drawing significant attention.
The paper is in the journal Advanced Materials. The team was led by Professor Jiwoong Yang in the Department of Energy Science and Engineering at DGIST and included Professor Moonkee Choi and Professor Jongnam Park of UNIST and Professor Daehyeong Kim of Seoul National University.
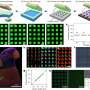
Professor Yang's team has recently developed, for the first time in the world, a new technology that enables the direct linkage of quantum dots, which are emerging as next-generation display materials, with stretchable polymers that can stretch like rubber.
Using this approach, they created a color-conversion layer that delivers high color reproducibility while maintaining performance even when stretched by more than 50%. By integrating this material with a micro-LED array, they successfully developed a stretchable micro-LED display capable of real-time pressure sensing.
Quantum dots are nanometer-sized materials that are capable of delivering vivid color reproduction and have recently been widely used in high-definition displays. However, when mixed with polymers for application in flexible displays, issues such as particle aggregation and color bleeding occur, thus limiting their commercialization.

To address this problem, Professor Yang's team bonded new molecules to the surface of eco-friendly quantum dots to form a cross-linking network that chemically connects them with stretchable polymers, thereby overcoming these challenges.
The color-conversion layer fabricated with this technology achieved a high resolution of 313 PPI while maintaining a color conversion efficiency of over 99% even when stretched by up to 50%. This represents the highest performance reported worldwide among related technologies to date.
The research team also integrated this color-conversion layer with micro-LEDs to realize a fully functional full-color stretchable display, and demonstrated its practical applicability by applying it to robotic skin and wearable health care monitoring sensors.
Professor Yang stated, "This research represents the world's first achievement that overcomes the limitations of existing quantum dot-based color conversion technologies while simultaneously satisfying both flexibility and resolution. It also holds great potential for expansion into diverse fields such as wearable electronics, robotic skin, smart health care, and human-machine interfaces."
More information: Kiwook Kim et al, Intrinsically‐Stretchable and Patternable Quantum Dot Color Conversion Layers for Stretchable Displays in Robotic Skin and Wearable Electronics, Advanced Materials (2025).
Journal information: Advanced Materials