Improving asphalt road pavement with nano-engineered particles
Warm mix asphalt (WMA) is gaining attention in the asphalt industry as an eco-friendly and sustainable technology.

Warm mix asphalt (WMA) is gaining attention in the asphalt industry as an eco-friendly and sustainable technology.

Jin Kim Montclare, professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering, with affilations at NYU Langone Health and NYU College of Dentistry, directed this research with first author Michael Meleties, fellow Ph.D. student Dustin ...

Researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) have demonstrated a technology that rapidly detects pollutants in water by measuring their impacts on swimming microorganisms.

The demand for flexible wearable electronics has spiked with the dramatic growth of smart devices that can exchange data with other devices over the internet with embedded sensors, software, and other technologies. Researchers ...

NUS researchers have discovered a method to fabricate a biologic interpenetrating network (IPN) hydrogel using applied rheology.

In a recent article in Sustainability, scientists from Reykjavik University (RU), the University of Gothenburg and the Icelandic Meteorological Office describe finding microplastic in a remote and pristine area of Vatnajokull ...

Researchers at MIT have developed a new method for determining the structure and behavior of a class of widely used soft materials known as weak colloidal gels, which are found in everything from cosmetics to building materials. ...
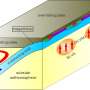
Earthquakes and volcanoes in subduction zones may cause great human catastrophe. Previous studies on subduction zone structure and causal mechanisms of giant megathrust earthquakes (M ≥ 9.0) have mainly focused on aspects ...
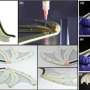
In a study published in Applied Materials Today, researchers from Singapore have developed the largest range of silicone and epoxy hybrid resins for the 3D printing of wearable devices, biomedical equipment, and soft robotics. ...

Adding a simple polymer to fertilizers or pesticides could dramatically reduce agricultural pollution, suggests a new study by researchers at the University of British Columbia.