Here's how origami could be used to shape the future of engineering
Folding a paper crane is a slow, methodical process. So is unfolding an array of solar panels in space.

Folding a paper crane is a slow, methodical process. So is unfolding an array of solar panels in space.

When a bird in flight lands, it performs a rapid pitch-up maneuver during the perching process to keep from overshooting the branch or telephone wire. In aerodynamics, that action produces a complex phenomenon known as dynamic ...
If you want to understand how the cell membrane works, Adam Cohen says, look no further than your kitchen.

An international team of scientists, including KAUST high performance computing experts and astronomers from the Paris Observatory and the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ), in collaboration with NVIDIA, is ...

Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) have expansive applications in biotechnology and advanced engineering with growing interest in materials science and engineering due to their potential in emerging systems. Existing techniques ...
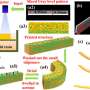
Reversible shape change is a highly desirable property for many biomedical applications, including mechanical actuators, soft robotics and artificial muscles. Some materials can change size or shape when irradiated with light, ...

Nanoporous metals are superior catalysts for chemical reactions due to their large surface area and high electrical conductivity, making them perfect candidates for applications such as electrochemical reactors, sensors and ...

In the world of materials, rigidity and elasticity are usually on opposite ends of the continuum. Typically, the more elastic a material, the less able it is to bear loads and resist forces. The more rigid it is, the more ...

New 3-D printed robotic structures can squeeze in tight spaces like a crack in the wall of a cave, jump over trip wire or crawl under a vehicle—all complex Army-relevant functions impossible for humans to perform safely.

Over the past 30 years, researchers have studied actuating materials that can reversibly change their volume under various stimuli in order to develop micro- and biomimetic robots, artificial muscles and medical devices.