High speed protein movies to aid drug design
Researchers from the University of Southampton have developed technology to help scientists observe proteins in motion. Understanding how proteins move will allow novel drugs to be designed.
See also stories tagged with Microfluidics

Researchers from the University of Southampton have developed technology to help scientists observe proteins in motion. Understanding how proteins move will allow novel drugs to be designed.

Scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), have developed a coin-sized chip that can directly isolate blood plasma from a tube of blood in just 30 minutes, which is more convenient and user-friendly ...
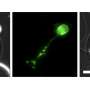
A team of scientists from Montana State University recently published unique research examining how individual cells respond to viral infection. The work used state-of-the-art technology to culture cells and track infection ...
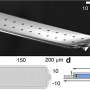
Fluidic force microscopy (FluidFM) combines the sensitivity of atomic force microscopy with microfluidics' capabilities, necessitating precise calibration of its cantilevers for reliable data. Traditional methods, however, ...
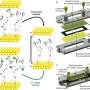
A new, greener, and cheaper method to accelerate chemical reactions has been developed by scientists at King's College London in collaboration with the University of Barcelona and ETH Zurich. Instead of using polluting and ...

Electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) cells, characterized by their self-emissive nature, have gathered significant interest for prospective display applications due to their uncomplicated structure and straightforward ...
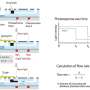
Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have engineered a new micro total analysis system that quantifies a target chemical in a microfluidic chip without pumps, tubes, and expensive detectors. The compound reacts ...
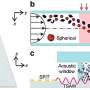
Thanks to the rapid progress in tiny tech, we've been mainly using microfluidics to sort tiny particles by size. But now, there's a new way to sort them by shape, which could be a big deal for medical tests and chemistry. ...
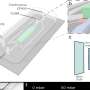
Porous materials are essential for many chemical processes, such as light harvesting, adsorption, catalysis, energy transfer, and even new technologies for electronic materials. Therefore, many efforts have been made to control ...

Over the past two decades, microfluidic devices, which use technology to produce micrometer-sized droplets, have become crucial to various applications. These span chemical reactions, biomolecular analysis, soft-matter chemistry, ...