Active deformation dynamics of cell nuclei contribute to the formation of intra-nuclear chromosome architectures
A Japanese researcher has investigated the contributions of active deformation dynamics of cell nuclei using the Brownian motion theory.
A Japanese researcher has investigated the contributions of active deformation dynamics of cell nuclei using the Brownian motion theory.

Particles floating in fluid perpetually flit about in all directions, a phenomenon referred to as Brownian motion. For example, proteins within our cells and pigment particles inside ink-jet printers wriggle and twitch their ...

UK scientists have pioneered a new way of manipulating several thousand atoms at a time, paving the way for building nanoscale electronic devices more quickly and easily at room temperature.

One of the striking features of self-organization in biomolecular systems is the capacity of assemblies of filamentous particles for synchronous motion. Â鶹ÒùÔºicists of Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich now provide new ...

For the first time ever, researchers have succeeded in creating arrangements of colloids – tiny particles suspended in a solution – and, importantly, they have managed to control their motion with high precision and speed. ...
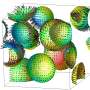
Researchers at the University of Tokyo have shown that in phase separation in liquids, as is seen when oil and water separate, occurs as a result of the ordered motion of droplets. Initially, a great number of small droplets ...

Classical Brownian motion theory was established over one hundred year ago, describing the stochastic collision behaviors between surrounding molecules. Recently, researchers from the Technical Institute of Â鶹ÒùÔºics and Chemistry, ...
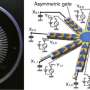
(Â鶹ÒùÔº)—Researchers have designed and implemented an algorithm that solves computing problems using a strategy inspired by the way that an amoeba branches out to obtain resources. The new algorithm, called AmoebaSAT, ...

Scientists have created microbe-sized beads that can utilize energy in the environment to self-propel upstream by purely physical means.
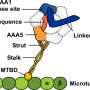
In research published in the Journal of Cell Biology, scientists from the RIKEN Brain Science Institute in Japan have made important steps toward understanding how dynein—a "molecular motor"—walks along tube-like structures ...