'Soft' nanoparticles give plasmons new potential
Bigger is not always better, but here's something that starts small and gets better as it gets bigger.
See also stories tagged with Colloidal gold
Bigger is not always better, but here's something that starts small and gets better as it gets bigger.

By examining tiny particles of gold with powerful X-ray beams, scientists hope they can learn how to cut down on harmful carbon monoxide emissions from motor vehicles.
Finding alternatives to antibiotics is one of the biggest challenges facing the research community. Bacteria are increasingly resistant to these drugs, and this resistance leads to the deaths of more than 25,000 around the ...
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to spread across the world, testing remains a key strategy for tracking and containing the virus. Bioengineering graduate student, Maha Alafeef, has co-developed a rapid, ultrasensitive ...

The quantum sensing abilities of nanodiamonds can be used to improve the sensitivity of paper-based diagnostic tests, potentially allowing for earlier detection of diseases such as HIV, according to a study led by UCL researchers ...

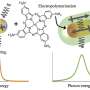
Today, optofluidics is one of the most representative applications of photonics for biological/chemical analysis. The ability of plasmonic structures (e.g., colloidal gold and silver nanoparticles, NPs) under illumination ...
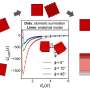
Materials scientists at Duke University have devised a simplified method for calculating the attractive forces that cause nanoparticles to self-assemble into larger structures.
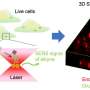
Successful drug development has a significant impact on people's quality of life worldwide. Being able to track how molecules get into target cells, and observing what they do when they are inside, is key to identifying the ...

Special anti-counterfeiting and chemical sensing tools that we can use with our eyes could be created thanks to a new nanoscale building method.

Current state-of-the-art techniques have clear limitations when it comes to imaging the smallest nanoparticles, making it difficult for researchers to study viruses and other structures at the molecular level.