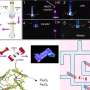
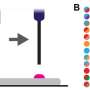
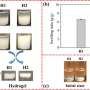
Tiny brick-busting 'muscles' for miniature robotics are sourced from wood
Wood is the source for a brick-breaking mini robotic muscle material developed by researchers in Sweden and Germany. The material—a specially-developed hydrogel—can shape-shift, expand and contract on demand when controlled ...