Making spintronic neurons sing in unison
What do fire flies, Huygens's wall clocks, and even the heart of choir singers, have in common? They can all synchronize their respective individual signals into one single unison tone or rhythm.

What do fire flies, Huygens's wall clocks, and even the heart of choir singers, have in common? They can all synchronize their respective individual signals into one single unison tone or rhythm.
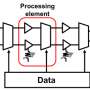
Toshiba Corporation continues to build on its commitment to promoting the Internet of Things and Big Data analysis with development of a Time Domain Neural Network (TDNN) that sues an extremely low power consumption neuromorphic ...
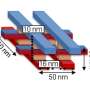
In 1959 renowned physicist Richard Feynman, in his talk "Plenty of Room at the Bottom," spoke of a future in which tiny machines could perform huge feats. Like many forward-looking concepts, his molecule and atom-sized world ...
(Â鶹ÒùÔº)—Researchers have developed a neuro-inspired analog computer that has the ability to train itself to become better at whatever tasks it performs. Experimental tests have shown that the new system, which is based ...
Engineers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst are leading a research team that is developing a new type of nanodevice for computer microprocessors that can mimic the functioning of a biological synapse—the place ...
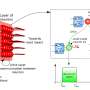
(Â鶹ÒùÔº)—When you hear a sound, only some of the neurons in the auditory cortex of your brain are activated. This is because every auditory neuron is tuned to a certain range of sound, so that each neuron is more sensitive ...

IBM scientists have created randomly spiking neurons using phase-change materials to store and process data. This demonstration marks a significant step forward in the development of energy-efficient, ultra-dense integrated ...
In experiments at two Department of Energy national labs – SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory – scientists at Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) have experimentally confirmed ...
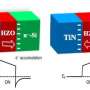
Scientists from MIPT have succeeded in growing ultra-thin (2.5-nanometre) ferroelectric films based on hafnium oxide that could potentially be used to develop non-volatile memory elements called ferroelectric tunnel junctions. ...

Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) today announced it will receive a first-of-a-kind brain-inspired supercomputing platform for deep learning developed by IBM Research. Based on a breakthrough neurosynaptic computer ...