New technique in which drugs make bacteria glow could help fight antibiotic resistance
A new technique could help reduce antibiotic prescribing by predicting which drugs could be effective in fighting bacteria within minutes.

A new technique could help reduce antibiotic prescribing by predicting which drugs could be effective in fighting bacteria within minutes.
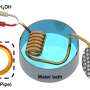
Researchers in Australia and China have proposed an innovative and cost-effective new method for creating silica beads, which have a number of key uses, ranging from nanomedicine and bioimaging to the production of paper ...
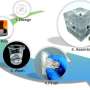
Scientists have recently engineered a modular system based on the Rubik's cube to design and reconfigure microfluidic systems. Research teams had previously pursued the arrangement of microfluidic blocks in diverse conformations ...

A device that monitors health conditions in the body using a person's sweat has been developed by Penn State and Xiangtan University researchers, according to Huanyu "Larry" Cheng, assistant professor of engineering science ...
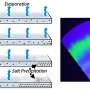
Human sweat contains several biomolecules the research community is exploring for noninvasive medical testing. Analyzing sweat for research, however, is often expensive, and devices typically are reliable for only a limited ...

Many species have naturally evolved remarkable strategies to visually adapt to their environments for protection and predation. Researchers have studied adaptive camouflaging in the infrared (IR) spectrum, although the method ...

At the PME department, a micro-sized pipette probe has been developed for handling multiple liquids. It is the first time that such a small probe can dose fluid volume, and simultaneously control the concentration of particles ...
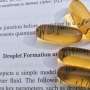
Microcapsules for the storage and delivery of substances are tiny versions of the type of capsule used for fish oil or other liquid supplements, such as vitamin D. A new method for synthesizing microcapsules, reported in ...

Bioengineers from UCLA and University of Tokyo have significantly increased the speed at which large liquid droplets, potentially containing individual live cells, can be sorted intact and in bulk.

Polysiloxane is an elastic polymer which is widely used in fluidics, optics, and biomedical engineering. It offers desirable properties for microfabrication due to its castable and curable properties.