Flexible gold sensor unlocks new generation of medical implants
A thin, flexible gold sensor engineered at The University of Queensland (UQ) has the potential to unlock the next generation of implantable medical devices.
See also stories tagged with Nanotechnology

A thin, flexible gold sensor engineered at The University of Queensland (UQ) has the potential to unlock the next generation of implantable medical devices.

Single-photon emitters are crucial building materials suited for optical quantum technologies. Among them, hexagonal boron nitride is a promising two-dimensional material that retains bright, room-temperature single-photon ...

The rapidly advancing field of nanophononics focuses on the study of hypersound, which are acoustic waves in the gigahertz to terahertz range, at the nanoscale. These high-frequency acoustic vibrations, also known as acoustic ...

Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have become a mainstay of the field of nanotechnology. Finding innovative applications across materials science, electronics, and medicine, CNTs have garnered a lot of attention from researchers in ...
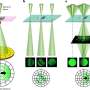
The group led by Professor Naoya Shibata of the University of Tokyo, in collaboration with Sony Group Corporation, succeeded in directly observing a two-dimensional electron gas that accumulated at the semiconductor interface.
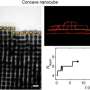
For the first time ever, researchers have watched the mesmerizing process of nanoparticles self-assembling into solid materials. In the stunning new videos, particles rain down, tumble along stairsteps and slide around before ...
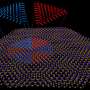
Cambridge researchers have discovered a new topological phase in a two-dimensional system, which could be used as a new platform for exploring topological physics in nanoscale devices.
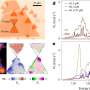
Novel, ultrathin nanomaterials exhibit remarkable properties. If you stack individual atomically thin layers of crystals in a vertical assembly, for example, fascinating physical effects can occur. For instance, bilayers ...
The human body is made up of thousands of tiny lymphatic vessels that ferry white blood cells and proteins around the body, like a superhighway of the immune system. It's remarkably efficient, but if damaged from injury or ...

When it comes to studying particles in motion, experimentalists have followed a 100-year-old theory that claims the microscopic motion of a particle is determined by random collisions with molecules of the surrounding medium, ...