Human retinas grown in a dish explain how color vision develops
Biologists at Johns Hopkins University grew human retinas from scratch to determine how cells that allow people to see in color are made.
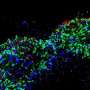
Biologists at Johns Hopkins University grew human retinas from scratch to determine how cells that allow people to see in color are made.
Human embryos start as a tiny mass of cells that are all the same. The first step in growing from a homogenous ball of cells into a complex individual with distinct organs and tissues is for the cells to divide into distinct ...

Invented over 50 years ago, flow cytometry-based cell sorting has become a widely used tool in biology labs for physically isolating cells based on their global surface marker expression profiles. But on August 27 in the ...
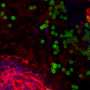
Washington State University researchers have developed a new approach for studying Cryptosporidium, a waterborne gastrointestinal parasite now recognized as one of the leading causes of potentially life-threatening diarrheal ...

For many years, drug development has relied on simplified and scalable cell culture models to find and test new drugs for a wide variety of diseases. However, cells grown in a dish are often a feint representation of healthy ...

New, higher-quality assemblies of great ape genomes have now been generated without the guidance of the human reference genome. The effort to reduce "humanizing" discovery bias in great ape genomes provides a clearer view ...
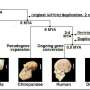
The evolution of larger brains in the last 3 million years played an important role in our ability as a species to think, problem-solve, and develop culture. But the genetic changes behind the expansion that made us human ...
Radio frequency identification (RFID) chips are used today for everything from paying for public transit to tracking livestock to stopping shoplifters. But now, researchers in the U.S. and Japan want to use them for something ...

Many neurological disorders—Alzheimer's, schizophrenia, autism, even depression—have lagged behind in new therapies. Because the brain is so complex, it can be difficult to discover new drugs and even when a drug is promising ...
Technologies such as RNA sequencing are now revealing which genes are expressed in each individual cell. All cells can then be arranged systematically using similar expression profiles. Dr. Jan Philipp Junker, head of the ...