New technique uses enzymes to create versatile nanoparticles
The selective bond-breaking powers of enzymes bring new versatility for building nanoparticles with a wide range of technical and medical potential.
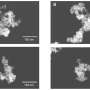
The selective bond-breaking powers of enzymes bring new versatility for building nanoparticles with a wide range of technical and medical potential.
The accelerated expansion of the present universe, believed to be driven by a mysterious dark energy, is one of the greatest puzzles in our understanding of the cosmos. The standard model of cosmology called Lambda-CDM, explains ...

Graphene has been called "the wonder material of the 21st century." Since its discovery in 2004, the material—a single layer of carbon atoms—has been touted for its host of unique properties, which include ultra-high ...

Graph states, a class of entangled quantum states that can be represented by graphs, have been the topic of numerous recent physics studies, due to their intriguing properties. These unique properties could make them particularly ...
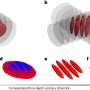
An international research team from Innsbruck and Geneva has, for the first time, probed the dimensional crossover for ultracold quantum matter. In the regime between one and two dimensions, the quantum particles perceive ...

At the intersection of chemistry and computation, researchers from the University of Glasgow have developed a hybrid digital-chemical probabilistic computational system based on the Belousov-Zhabotinsky (BZ) reaction which ...

Researchers at DTU have successfully distributed a quantum-secure key using a method called continuous variable quantum key distribution (CV QKD). The researchers have managed to make the method work over a record 100 km ...

Researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory have demonstrated that advanced quantum-based cybersecurity can be realized in a deployed fiber link.
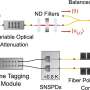
Scientists at Paderborn University have used a new method to determine the characteristics of optical quantum states. For the first time, they are using certain photon detectors—devices that can detect individual light ...

Some 13.8 billion years ago, the universe began with a rapid expansion we call the Big Bang. After this initial expansion, which lasted a fraction of a second, gravity started to slow the universe down. But the cosmos wouldn't ...