New silicon nanowires can really take the heat
Scientists have demonstrated a new material that conducts heat 150% more efficiently than conventional materials used in advanced chip technologies.Â

Scientists have demonstrated a new material that conducts heat 150% more efficiently than conventional materials used in advanced chip technologies.Â
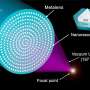
Rice University photonics researchers have created a potentially disruptive technology for the ultraviolet optics market.

An independent researcher and one scientists from the University of Tennessee and one from Ancient Art Archive have revealed ancient Native American artwork inscribed on cave walls and ceilings in Alabama using 3D photogrammetry. ...
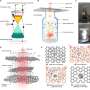
High-entropy nanoalloys (HENA) have widespread applications in materials science and applied physics. However, their synthesis is challenging due to slow kinetics that cause phase segregation, sophisticated pretreatment of ...

Shine a flashlight into a murky pond water and the beam won't penetrate very far. Absorption and scattering rapidly diminishes the intensity of the light beam, which loses a fixed percentage of energy per unit distance traveled. ...
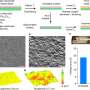
The development of new, more efficient electrochemical cells could provide a good option for carbon-free hydrogen and chemical production along with large-scale electricity generation and storage.Â
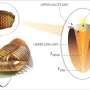
Five hundred million years ago, the oceans teemed with trillions of trilobites—creatures that were distant cousins of horseshoe crabs. All trilobites had a wide range of vision, thanks to compound eyes—single eyes composed ...

The world sits on the brink of a major ecological disaster and the need for renewable energy sources has never been more urgent. Perhaps the most significant source of untapped renewable energy is, unsurprisingly, the Sun. ...
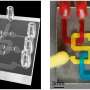
Microfluidic devices are compact testing tools made up of tiny channels carved on a chip, which allow biomedical researchers to test the properties of liquids, particles and cells at a microscale. They are crucial to drug ...

A breakthrough in quantum imaging could lead to the development of advanced forms of microscopy for use in medical research and diagnostics.