Turning cells into computers with protein logic gates
The same basic tools that allow computers to function are now being used to control life at the molecular level. The advances have implications for future medicines and synthetic biology.
See also stories tagged with Biological Engineering
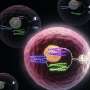
The same basic tools that allow computers to function are now being used to control life at the molecular level. The advances have implications for future medicines and synthetic biology.
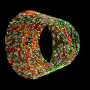
During the progression of pulmonary hypertension, structural and functional changes in the small muscular arteries play a significant role and contribute to the disease. Bioengineers aim to develop advanced, anatomically ...
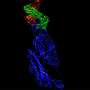
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) scientists are contributing to the global fight against COVID-19 by combining artificial intelligence/machine learning, bioinformatics and supercomputing to help discover candidates ...

Stanford researchers have developed a technique that reprograms cells to use synthetic materials, provided by the scientists, to build artificial structures able to carry out functions inside the body.

Proteins are the building blocks of life, and consequently, scientists have long studied how they can improve proteins and design completely new proteins that perform new functions and processes.

Life is rife with patterns. It's common for living things to create a repeating series of similar features as they grow: think of feathers that vary slightly in length on a bird's wing or shorter and longer petals on a rose.
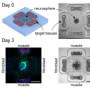
Scientists watched the formation of a self-emergent machine as stem cell-derived neurons grew toward muscle cells in a biohybrid machine, with neural networks firing in synchronous bursting patterns. The awe-inspiring experiment ...

Bioengineers at the University of California San Diego have redesigned how harmless E. coli bacteria "talk" to each other. The new genetic circuit could become a useful new tool for synthetic biologists who, as a field, are ...

Recent advances in bioengineering and computational modeling have given researchers the ability to examine complex biological processes with molecular-level detail.

When it comes to testing drinking water for dangerous contaminants, such as heavy metals like lead or cadmium, continuous testing directly from faucets people drink from is important. Yet, very little of this kind of water ...