Researchers identify a cheaper, more convenient method to detect asbestos
For decades, a laboratory procedure known as transmission electron microscopy (TEM) has been used to test for asbestos in samples taken at construction sites.
See also stories tagged with Transmission electron microscopy

For decades, a laboratory procedure known as transmission electron microscopy (TEM) has been used to test for asbestos in samples taken at construction sites.

A study has unlocked new dimensions in understanding the ultrafast processes of charge and energy transfer at the microscale. The research delves into the dynamics of microscopic particles, providing insights that could revolutionize ...

A team led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has invented a technique to study electrochemical processes at the atomic level with unprecedented resolution and used it to gain new insights into a popular ...

They say that one can miss the forest for the trees. But it's often worth taking a closer look at the trees to make sense of the dense, brambly whole. That's what a Stanford University group did to tackle a thorny quantum-information ...
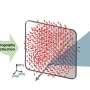
Materials that can maintain a magnetized state by themselves without an external magnetic field (i.e., permanent magnets) are called ferromagnets. Ferroelectrics can be thought of as the electric counterpart to ferromagnets, ...
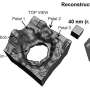
National University of Singapore (NUS) physicists have developed a computational imaging technique to extract three-dimensional (3D) information from a single two-dimensional (2D) electron micrograph. This method can be readily ...
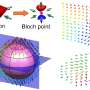
A Bloch point is a singular point around which the field vectors are oriented in nearly all directions. In magnetics, it is the natural link between classical and quantum magnetism, and it has not been directly observed. ...

Lighting a gas grill, getting an ultrasound, using an ultrasonic toothbrush—these actions involve the use of materials that can translate an electric voltage into a change in shape and vice versa.
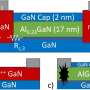
The scorching surface of Venus, where temperatures can climb to 480°C (hot enough to melt lead), is an inhospitable place for humans and machines alike. One reason scientists have not yet been able to send a rover to the ...

A low-cost, tin-based catalyst can selectively convert carbon dioxide to three widely produced chemicals—ethanol, acetic acid and formic acid.