New shape memory polymer represents biomedical breakthrough
Researchers in the College of Engineering and Computer Science have developed a material—a new kind of shape memory polymer (SMP)—that could have major implications for health care.

Researchers in the College of Engineering and Computer Science have developed a material—a new kind of shape memory polymer (SMP)—that could have major implications for health care.
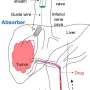
With the help of sponges inserted in the bloodstream to absorb excess drugs, doctors are hoping to prevent the dangerous side effects of toxic chemotherapy agents or even deliver higher doses to knock back tumors, like liver ...
For hundreds of millions of years, plants thrived in the Earth's oceans, safe from harsh conditions found on land, such as drought and ultraviolet radiation. Then, roughly 450 million years ago, plants found a way to make ...

Researchers at McMaster University have solved a vexing problem by engineering surface coatings that can repel everything, such as bacteria, viruses and living cells, but can be modified to permit beneficial exceptions.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a condition in which plaque forms on the walls of coronary arteries, causing them to narrow. Eventually, this could lead to a heart attack, or death. This condition is now the single largest ...

Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) have expansive applications in biotechnology and advanced engineering with growing interest in materials science and engineering due to their potential in emerging systems. Existing techniques ...
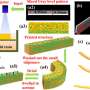
Reversible shape change is a highly desirable property for many biomedical applications, including mechanical actuators, soft robotics and artificial muscles. Some materials can change size or shape when irradiated with light, ...

Implantation of a stent-like flow diverter can offer one option for less invasive treatment of brain aneurysms—bulges in blood vessels—but the procedure requires frequent monitoring while the vessels heal. Now, a multi-university ...
A few years ago, two researchers took the 50 most-used ingredients in a cook book and studied how many had been linked with a cancer risk or benefit, based on a variety of studies published in scientific journals.
New research shows companies cut funding for research and development in response to a tax imposed on medical devices as part of the Affordable Care Act.