The 2020 elections will determine which voices dominate public land debates

Presidential elections are anxious times for federal land agencies and the people they serve. The , , and manage more than , which means that a new president can literally reshape the American landscape.
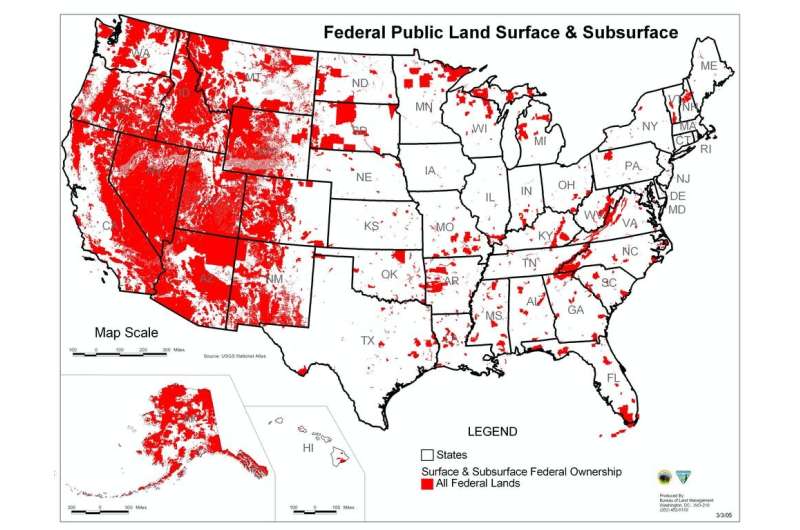
Federal influence is particularly significant in the Western U.S. Across the 11 states from the Rocky Mountains to the Pacific Coast, the federal government owns . In Alaska it owns over 60%.
Voters have a striking choice this year. President Donald Trump entered office committed to the "." His administration raced to reduce environmental planning and regulations and expand private development in pursuit of "."
In contrast, Vice President Biden's campaign proposals for public lands remain fairly broad, but are largely consistent with the Obama administration's priorities. The most significant difference is Biden's pledge to .
How would each candidate fulfill these promises? As I explain in my new book, "," public lands are a microcosm of today's polarized American politics.
On the right, mainstream conservatives and industrial corporations want reduced regulation and increased resource development, while a more militantly anti-federal element of the Republican Party demands an end to public land ownership altogether. On the left, mainstream Democrats want carefully regulated land management with , but a vocal progressive wing is demanding that the federal government . These tensions raise questions about how far each candidate would go.
The Trump administration is expected on Friday to finalize its plan to open about 9 million acres of Alaska's Tongass National Forest to logging and road construction.
— The New York Times (@nytimes)
Republicans: Less regulation, more development
Since Ronald Reagan ran 40 years ago as a "" who supported turning control of public lands back to Western states, Republicans have coalesced around a set of . They include reducing federal regulation, limiting the scope of environmental reviews and increasing natural resource development.
This approach has drawn support from natural resource industries, resource-dependent communities and a growing body of , , , and . Their core libertarian conviction is that reducing government leads to prosperity.
The Trump administration has championed these priorities through actions that include shrinking several national monuments to expand oil leasing; preparing to ; and . The full impact of these actions is hard to assess, since many face challenges in court, where the administration has . But their theme is clear: Public lands are .
As part of this effort, the Trump administration moved the Bureau of Land Management's headquarters from Washington, D.C., to Grand Junction, Colorado. The agency has , which it shares with several oil and gas companies.
A vocal element of the Republican Party challenges the federal government's authority to own and manage public lands at all. Some advocates have engaged in with federal authorities. Several Western states have over the past decade demanding that the federal government transfer ownership of public lands and mineral rights to them.
President Trump has catered to this extreme wing while stopping short of meeting its explicit demands. He signaled support by appointing conservative activist William Perry Pendley as the Bureau of Land Management's functional acting director in July 2019—a step that a federal court in Montana recently because it bypassed a confirmation hearing. Pendley was known for and years of litigation over public land management.
The president also has pardoned controversial figures who are embraced by opponents of public land authority, including former Arizona Sheriff Joe Arpaio and two convicted of arson on federal property.
Despite his administration's losses in court, I expect that if President Trump is reelected he will continue down this path of deregulation, resource development and deference to conservative Western interests, with occasional gestures of support to more radical conservatives.
Democrats: Scientific management with limited development
Recent Democratic presidents, from Jimmy Carter to Barack Obama, have that guide public land management, such as the National Environmental Policy Act and the Endangered Species Act. Democratic administrations have emphasized scientific monitoring and regulatory oversight while still supporting energy development and other commercial resource uses of public lands.
Vice President Biden's long and suggestthat he will continue this approach. Biden has promised to , and manage energy development on public lands in ways that and gradually .
But a Biden administration would face tensions within the Democratic Party as well. Progressives are calling for , including for oil and gas production and on new oil, gas and coal leases on public lands. Biden has signaled for this agenda, but insists that hydraulic fracturing and fossil fuel development .
A Biden administration, then, would likely seek to and push beyond it with tighter limits on fossil fuel production.
Everybody loves the outdoors
These sharply different visions can obscure the fact that there is substantial commitment to public lands, especially as places for hunting, fishing, camping and other recreational uses. This consensus was evident when Congress passed the in July with strong bipartisan support. With an eye on election polls, President Trump bragged that signing the bill made him the .
As I see it, this bill was popular because it did not address controversial questions like regulation or energy development. Instead it provided billions of dollars for maintaining roads, trails, visitor centers and other public land infrastructure. It also guaranteed permanent funding for the , which uses money from federal fossil fuel royalties to protect valuable lands and waters from development.
That pairing suggests that public land ownership and fossil fuel development will both be part of the next administration. But the election will determine how these resources will be managed, and who will have the most influence over this process.
Provided by The Conversation
This article is republished from under a Creative Commons license. Read the .![]()



















