Seven times people discovered the Americas. How they got there

When Columbus landed in 1492, the Americas had been settled for tens of thousands of years. He wasn't the first person to discover the continent. Instead, his discovery was the last of many discoveries.
In all, people found the Americas at least seven different times. For at least six of those, it wasn't so new after all. The discoverers came by sea and by land, bringing new genes, new languages, new technologies. Some stayed, explored, and built empires. Others went home, and left few hints they'd ever been there.
From last to first, here's the story of how we discovered the Americas.
7. Christopher Columbus: AD 1492
In 1492, Europeans could reach Asia by the , or by sailing the Cape Route around the southern tip of Africa. Sailing west from Europe was thought to be impossible.
The ancient Greeks had accurately calculated that the circumference of the Earth was , which put Asia far to the west. But Columbus botched his calculations. An error in unit conversion gave him a circumference of just 30,000 km.
This mistake, with other assumptions born of wishful thinking, gave a distance of just from Europe to Japan. The actual distance is almost 20,000 kilometers.
So Columbus's ships set sail without enough supplies to reach Asia. Fortunately for him, he hit the Americas. Columbus, thinking he'd found the East Indies, called its people "Indios," or Indians. He ultimately died without realizing his mistake. It was the navigator Amerigo Vespucci who realized Columbus had and in 1507 the name America was applied in Vespucci's honor.

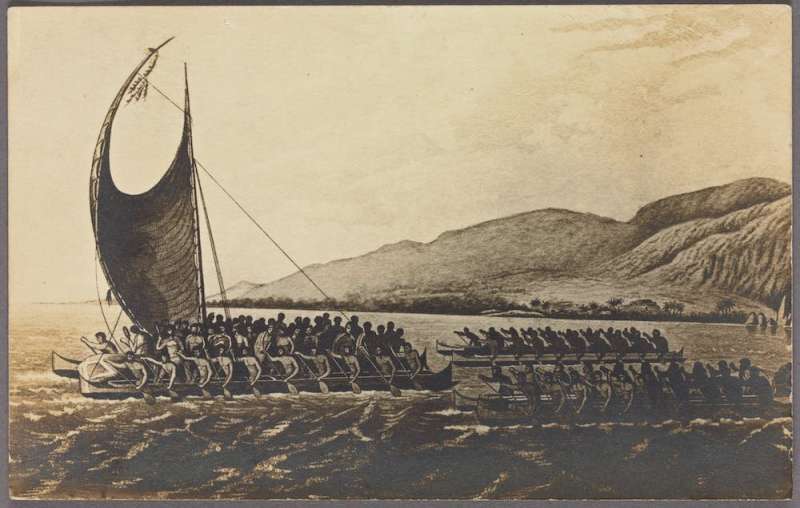
6. Polynesians: AD 1,200
Around 2,500 BC, a seafaring people to find new lands. They sailed south through the Philippines, east through Melanesia, then out into the vast South Pacific. These people, the , were master navigators, reading wind, waves and stars to cross thousands of kilometers of open ocean.
Using huge double canoes, the Polynesians Samoa, Fiji, Tonga, and the Cook Islands. Some went , becoming . Others went east to Tahiti, Hawaii, Easter Island, and the Marquesas. From here, they at last hit South America. Then, having explored most of the Pacific, they gave up exploration and forgot South America entirely.
But evidence of this remarkable voyage remained. The South Americans acquired , while the Polynesians may have picked up . And they shared more than food. Eastern Polynesians have . Polynesians didn't just meet Native Americans, they married them.
5. Norse: AD 1,021
According to Viking sagas, around AD 980, , fierce Viking and cunning salesman, named a vast, icy wasteland "Greenland" to . Then, in AD 986, a boat from Greenland .
Around , Erik's son Leif established a settlement in Newfoundland. The Vikings struggled with the harsh climate, before war with Native Americans ultimately forced them back to Greenland. These stories were long dismissed as myths, until 1960, when archaeologists dug up the remains of .

4. Inuit: AD 900
Just before the Vikings, the Inuit people traveled in skin boats. Hunting whales and seals, living in sod huts and igloos, they were well adapted to the cold Arctic Ocean, and skirted its shores all the way to Greenland.
Curiously, their DNA is , implying their ancestors colonized Asia from Alaska, then went back to discover the Americas again.
3. Eskimo-Aleut: 2,000–2,500 BC
The Inuit descend from an earlier migration: that of speakers of the . These are distinct from other Native American languages, and might even be distantly related to Uralic languages such as .
This, with DNA evidence, suggests the Eskimo-Aleut was a distinct migration. They came across the from present-day Russia to Alaska, perhaps years ago, partly displacing and mixing with earlier migrants: the Na-Dene people.
2. Na-Dene: 3,000–8,000 BC
Another group, the Na-Dene, crossed the Bering Sea to Alaska around , although other studies suggest they settled the Americas as long as .
links them not to modern people in the Eskimo-Aleut group, but to Native Americans speaking the Na-Dene language family, such as the , , , and Apache people. Na-Dene languages are closest to languages , suggesting again that they represent a distinct migration.

1. First Americans: 16,000–35,000 years ago
Almost all Native American tribes—Sioux, Comanche, Iroquois, Cherokee, Aztec, Maya, Quechua, Yanomani, and dozens of others—speak . That suggests their languages evolved from a common ancestor tongue, spoken by a single tribe entering the Americas long ago. Their descendants' low genetic diversity suggests this founding tribe was small, maybe .
How did they get there? Before the last ice age ended 11,700 years ago, so much water was that sea levels fell. The bottom of the Bering Sea dried out, creating the . America's first people just walked from Russia to Alaska. But the timing of their migration is controversial.
Archaeologists once thought the , living , were the . But evidence humans arrived in the Americas much earlier.
Finds in , , , the , and suggest people reached the Americas long before the Clovis people.
date to 23,000 years ago. in a Mexican cave may date to 32,000 years ago. A from Colorado dates to 31,000–38,000 years ago. And traces of fire put 32,000 years ago.
Some of these dates could be incorrect, but with each new discovery it seems increasingly unlikely that they're all wrong.
An early migration would neatly solve a major mystery. 13,000 years ago, a vast glacier, the , buried Canada in ice up to three kilometers thick. If people arrived in North America then, how did they cross the ice? Southeast Alaska's rugged coast, full of glaciers and fjords, was likely impassible, and early Americans probably lacked boats. But 30,000 years ago, the ice sheet hadn't fully formed.
Before the ice spread, people could have hunted mammoths and horses east from Alaska into the Northwest Territories, then south through Alberta and Saskatchewan into Montana. Remarkably, humans may have settled the Americas . Yet that might make sense. Alaska's Arctic is harsh, but Europe had .

The end of discovery
1492 was the last discovery of the Americas. Following the voyages of Columbus, Magellan, and Cook, the scattered descendants of humanity's diaspora were finally reunited. Aside from a few , everywhere was known to everyone. Discovery was impossible.
But the story of the Americas' settlement is still being written, and our understanding is evolving. The Eskimo-Aleut may have been , not one. Genes of other, early founding populations. And given how little evidence the Polynesians and Norse left of their visits, it's conceivable there were other migrations, ones of which we have little evidence.
There's so much we don't know. No one can discover the Americas anymore, but there's a lot left to discover about their discovery.
Provided by The Conversation
This article is republished from under a Creative Commons license. Read the .![]()