Earliest glass workshop north of the Alps discovered
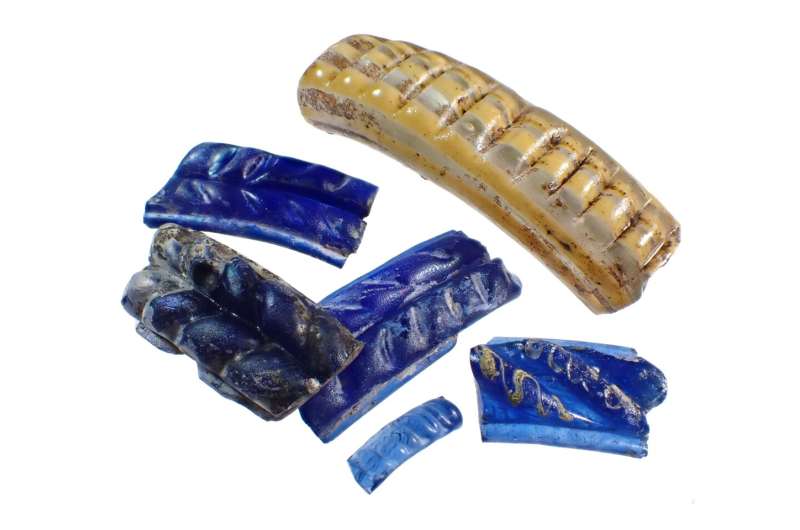

After 20 years of above-ground surveys, archaeologists have excavated the famous Iron Age site of Němčice and confirmed the presence of the earliest glass workshop north of the Alps.
Němčice is one of the most important settlement sites of the La Tène Period (3rd–2nd century BC) in Central Europe, famous for its unprecedented amount of gold and silver coins which number over 2,000.
Numerous beautiful glass bracelets and beads have also been found at the site. As such, it was thought that Němčice was a center of glass production, but only these excavations have confirmed this fact.
"No one yet knows how exactly the Celts made glass bracelets," said author of the research, Dr. Ivan Čižmář from the Institute of Archaeological Heritage Brno.
"Therefore, we were interested in anything that tells us something about the technology of production."
To attempt to answer this question, Dr. Čižmář and a team from the Institute of Archaeological Heritage Brno excavated an area where large amounts of glass objects had been found on the surface, hoping to find evidence of glass production. Their astonishing results are published in the journal Antiquity.
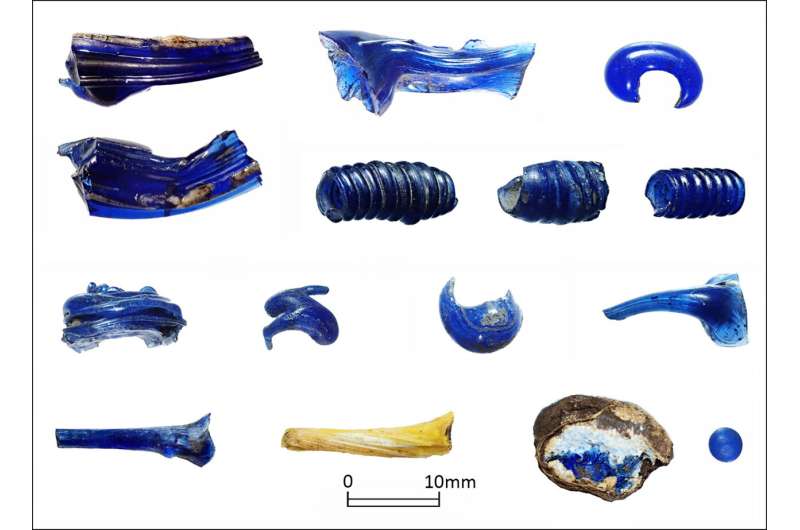
While tools used to make glass were not found, a mixture of complete and partially complete glass products were discovered. This indicates that glass was produced at Němčice.
Not only glass beads and bracelets were found during the excavation, but also amber pieces, likewise in various stages of completion. This confirms that the complex was associated with multiple materials of production, making it even more regionally important.
At the same time, researchers excavated a square area of Němčice identified by geophysical survey at the highest part of the site. It has many similarities with possible ritual structures from Austria, implying shared beliefs in Central Europe.
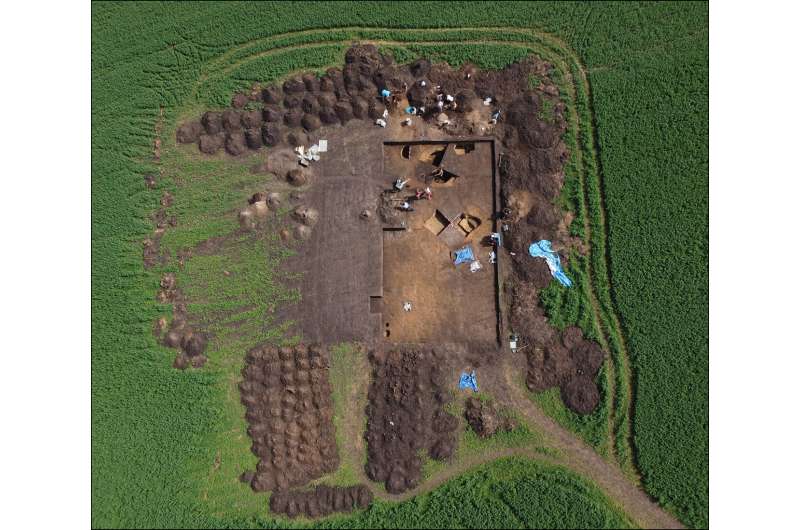

According to Dr. Čižmář, "The presence of these likely sacred features at Němčice indicates the character of the site not only as a trade and production center, but also as a seat of an elite and a ritual center."
Importantly, the possibility of Němčice being a center of production and shared beliefs would indicate that it was part of a wider Central European network along the "Amber Road"—an important trade route between Northern and Southern Europe.
More information: Ivan Čižmář et al, Němčice: research at a key La Tène site in Moravia, Antiquity (2023).
Journal information: Antiquity
Provided by Antiquity





















