Nanoscale material offers new way to control fire
High-temperature flames are used to create a wide variety of materials—but once you start a fire, it can be difficult to control how the flame interacts with the material you are trying to process. Researchers have now developed a technique that utilizes a molecule-thin protective layer to control how the flame's heat interacts with the material—taming the fire and allowing users to finely tune the characteristics of the processed material.
"Fire is a valuable engineering tool—after all, a blast furnace is only an intense fire," says Martin Thuo, corresponding author of a paper on the work and a professor of materials science and engineering at North Carolina State University. "However, once you start a fire, you often have little control over how it behaves."
"Our technique, which we call inverse thermal degradation (ITD), employs a nanoscale thin film over a targeted material. The thin film changes in response to the heat of the fire, and regulates the amount of oxygen that can access the material. That means we can control the rate at which the material heats up—which, in turn, influences the chemical reactions taking place within the material. Basically, we can fine-tune how and where the fire changes the material."
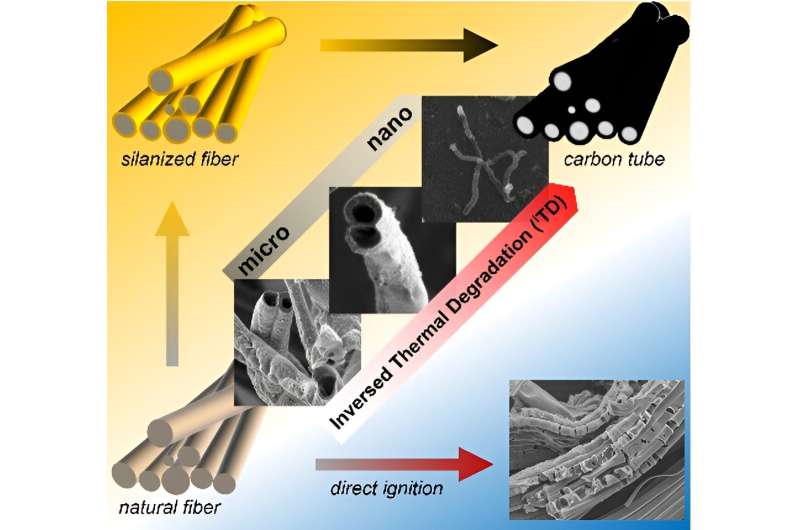
Here's how ITD works. You start out with your target material, such as a cellulose fiber. That fiber is then coated with a nanometer thick layer of molecules. The coated fibers are then exposed to an intense flame. The outer surface of the molecules combusts easily, raising the temperature in the immediate vicinity.
But the inner surface of the molecular coating chemically changes, creating an even thinner layer of glass around the cellulose fibers. This glass limits the amount of oxygen that can access the fibers, preventing the cellulose from bursting into flames. Instead, the fibers smolder—burning slowly, from the inside out.
"Without the ITD's protective layer, applying flame to cellulose fibers would just result in ash," Thuo says. "With the ITD's protective layer, you end up with carbon tubes."
"We can engineer the protective layer in order to tune the amount of oxygen that reaches the target material. And we can engineer the target material in order to produce desirable characteristics."
The researchers conducted proof-of-concept demonstrations with cellulose fibers to produce microscale carbon tubes.
The researchers could control the thickness of the carbon tube walls by controlling the size of the cellulose fibers they started with; by introducing various salts to the fibers (which further controls the rate of burning); and by varying the amount of oxygen that passes through the protective layer.
"We have several applications in mind already, which we will be addressing in future studies," Thuo says. "We're also open to working with the private sector to explore various practical uses, such as developing engineered carbon tubes for oil-water separation—which would be useful for both industrial applications and environmental remediation."
The work is published in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
More information: Chuanshen Du et al, Spatially Directed Pyrolysis via Thermally Morphing Surface Adducts, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2023).
Journal information: Angewandte Chemie International Edition
Provided by North Carolina State University