Chemical engineers provide new insights in COâ‚‚ conversion with electricity

Researchers from the Department of Chemical Engineering at the University of Twente, led by Georgios Katsoukis, have discovered how the chemical environment around copper electrodes can dramatically influence the conversion of carbon dioxide (COâ‚‚) into formate. This discovery can help improve the selectivity in COâ‚‚ reduction reactions, offering new insights into how to control these processes more effectively.
One of the ways to create a more sustainable and circular economy is to capture CO2 emissions and transform them into useful resources. But to do so, these CO2 reduction technologies need to be optimized and far more efficient.
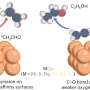
In this study, in ACS Catalysis, the research team investigated how COâ‚‚ reacts at the surface of copper electrodes in an aqueous environment. By altering the pH near the electrode, the team discovered that the local chemical environment is crucial in determining how quickly and efficiently COâ‚‚ can be converted into formate, a useful chemical with many industrial applications.
Selectivity in COâ‚‚ reduction reactions has been a longstanding challenge, as multiple products can form depending on the reaction conditions. This finding challenges the traditional focus on catalyst material alone and emphasizes the importance of optimizing the surrounding chemical conditions.
This research highlights the importance of controlling the chemical environment in CO2 reduction processes to improve selectivity and efficiency. By fine-tuning the condition around the copper electrode, it may be possible to enhance the selectivity toward desired products such as formate.
At the same time, it could also extend the life of the electrode. These advancements could play a crucial role in developing more efficient carbon dioxide conversion systems.
The findings from this study provide a blueprint for future research and the development of COâ‚‚ reduction technologies. By focusing on the optimization of the chemical environment, in addition to the catalyst, scientists can work towards creating more selective and efficient systems.
This approach brings us closer to practical solutions for transforming COâ‚‚ emissions into useful resources, fostering a more sustainable and circular economy.
More information: Georgios Katsoukis et al, Time-Resolved Infrared Spectroscopic Evidence for Interfacial pH-Dependent Kinetics of Formate Evolution on Cu Electrodes, ACS Catalysis (2024).
Journal information: ACS Catalysis
Provided by University of Twente