Antithrombin study proposes new mechanism of action for the plasma protein's functional role

Antithrombin, a plasma protein, has been reported to control thrombin activity by directly binding to thrombin, as well as to have an anti-inflammatory effect. However, the actual molecular mechanism of the anti-inflammatory effect of antithrombin was completely unknown.
In a on HRG, Professor Nishibori's research group succeeded in identifying a new HRG-specific receptor, and based on a similar idea, they hypothesized that antithrombin has a plasma membrane receptor related to its anti-inflammatory effect.
Using a screening method developed independently by Professor Sakaguchi's research group, they conducted a search for and identification of a new receptor for antithrombin and analyzed its function.
Antithrombin ligands and candidate receptor genes were co-expressed in HEK293T cells, and the candidate receptors bound to the ligand were identified by immunoprecipitation.
The research is in the journal Blood Vessels, Thrombosis & Hemostasis.
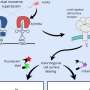
As a result, CLEC1A was identified as a candidate receptor for antithrombin. Antithrombin stimulates CLEC1A on human neutrophil cells to change the morphology of neutrophils to a spherical shape with a smooth surface, and functionally suppresses neutrophil cell death and ROS production.
They also demonstrate that the antithrombin-CLEC1A system is involved in the anti-inflammatory action of antithrombin. This cellular effect of antithrombin is very similar to that of HRG, which has the same CLEC1A as its receptor, suggesting a completely new functional role and mechanism of action for this plasma protein group.
This research proposes a completely new mechanism of action, cell plasma membrane receptor stimulation, for the functional role of the plasma protein antithrombin. Not only is the innovative method of receptor identification academically unique, but it is expected to bring about revolutionary changes in plasma protein science through its application to other plasma protein factors in the future.
More information: Yohei Takahashi et al, Antithrombin regulates neutrophil activities through the stimulation of C-type lectin family 1A, Blood Vessels, Thrombosis & Hemostasis (2024).
Provided by Okayama University