Researchers create high-resistant starch rice by impaired amylopectin synthesis

Rice is one of the most important staple crops and an excellent starch-provider. Resistant starch (RS) has shown beneficial effects on diabetes, weight management and inflammatory bowel disease.
Most rice cultivars only contain an RS level lower than 2% in cooked rice. Now, a group of scientists have shown that the mutations of specific amylopectin biosynthetic genes could further increase the RS content in the soluble starch synthase IIIa (ssIIIa) ssIIIb background, providing insights into the RS biosynthesis in rice.
This study, conducted by Wang Anqi and colleagues from Prof. Li Jiayang's team from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, was online on Nov. 19 in Plant Biotechnology Journal titled "Creation of high-resistant starch rice through systematic editing of amylopectin biosynthetic genes inrs4."
"Elucidating the mechanism of RS biosynthesis has important theoretical and practical significance for improving the nutritional value of rice," said Prof. Li.
Previous research by Li's team and their collaborators has shown that single mutant ssIIIa and double mutant ssIIIassIIIb could increase the RS content from 2% to 6% and 10%, respectively.
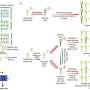
In their new study, the researchers used genome editing to conduct a systematic genetic analysis of 14 amylopectin biosynthetic genes in the ssIIIa ssIIIb double mutant background. The mutation of specific amylopectin biosynthetic genes further increased the RS content in the ssIIIa ssIIIb background.
The quadruple mutants of sbeI sbeIIb ssIIIa ssIIIb and sbeI ssIVb ssIIIa ssIIIb could boost RS levels to more than 18%, the study found.
The eating quality of cooked rice and grain yield decreased as RS contents increased, indicating a trade-off between these traits. While in these mutants, the ssIIIa ssIIIb mutant demonstrated balanced RS and grain yield.
"Our study shed light on RS biosynthesis by identifying a number of amylopectin biosynthetic genes and developing practical ways for breeding high-RS rice varieties with balanced performance," said Prof. Li.
More information: Anqi Wang et al, Creation of high鈥恟esistant starch rice through systematic editing of amylopectin biosynthetic genes in rs4, Plant Biotechnology Journal (2024).
Journal information: Plant Biotechnology Journal
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences