Antiferromagnetic neuromorphic memory: New spintronic device achieves brain-like memory and processing

A research team led by Prof. Long Shibing from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has, for the first time, made spintronic neuromorphic devices based on CoO/Pt heterostructure. The study is in Nano Letters.
Spintronics devices have attracted great attention due to their low power consumption, high operation speed and radiation resistance. Antiferromagnetic (AFM) materials, with their atomic-scale alternating magnetic moment distribution, are ideal candidates for developing spintronic neuromorphic devices. However, constructing AFM neuromorphic devices is still a challenge.
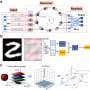
First, researchers attained out-of-plane magnetic anisotropy based on CoO/Pt heterostructure with (111) orientation. By measuring the Hall resistance, researchers confirmed the device's strong perpendicular anisotropy according to the first principle calculation.
The team achieved the device's nonlinear features of magnetization reversal, as well as its self-relaxation under thermal activation. Due to the rotatable regime of ultra-thin CoO, the CoO/Pt material of the device well reflects magnetization reversal.
The reversal of activated magnetic domains in the device determines its relaxation behavior, which is related to its short-term memory capability. In addition, researchers controlled the sweeping speed of the magnetic field to better identify the long-term memory in the system.
Based on these results, the neuromorphic device demonstrates nonlinear response and short-term memory, realizing its all-electrical readout and writing.
The researchers also proved that this device can exhibit a high recognition accuracy in reservoir computing tasks, such as handwritten digit recognition and quantum state classification. The recognition accuracy is effectively improved by passing the pulse sequence through the nonlinear AFM device.
The team has proposed and verified its unique advantages in multi-dimensional information processing. On the basis of its bidirectional relaxation properties, the device enables ternary encoding and accurately recognizes information in the additional dimension.
The study lays the foundation for further leveraging AFM materials to develop neuromorphic computing systems with ultrahigh speed and ultracompact integration.
More information: Xueqiang Xiang et al, An Antiferromagnetic Neuromorphic Memory Based on Perpendicularly Magnetized CoO, Nano Letters (2024).
Journal information: Nano Letters
Provided by University of Science and Technology of China