Novel model optimization algorithm improves robustness of near-infrared spectroscopy models

Lisa Lock
scientific editor

Robert Egan
associate editor

A research team from the Hefei Institutes of Â鶹ÒùÔºical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has proposed a novel model optimization algorithm—External Calibration-Assisted Screening (ECA)— that significantly enhances the prediction robustness of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) quantitative models. The findings are in Analytica Chimica Acta.
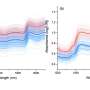
Near-infrared spectroscopy, as a highly promising non-destructive analytical method, relies heavily on the development level of its calibration models for prediction effectiveness. However, variations in measurement conditions often cause substantial prediction deviations. Consequently, mature NIRS models require strong robustness against environmental interference.
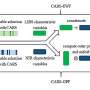
In this study, the researchers proposed a paradigm shift toward robustness-oriented optimization (rather than mere accuracy) for NIRS models and introduced ECA as its implementation pathway.
The ECA method rapidly adapts initial models to new detection environments by calibrating them with externally collected samples under novel measurement conditions. The researchers innovatively integrated cross-validation results with external calibration results to establish a new robustness evaluation metric, PrRMSE, to identify the optimally robust model through multi-parameter modeling combination screening.
To further boost performance, they combined ECA with an established competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS) algorithm, resulting in a hybrid optimization framework named ECCARS.
The ECCARS framework was validated using one laboratory-measured rice flour dataset and two public corn datasets. The results were impressive: compared with traditional CARS methods, ECCARS-selected models achieved a 12.15% to 725% reduction in calibration errors, and a 27.63% to 482% reduction in validation errors under varying conditions.
These results confirm that ECCARS dramatically improves the robustness and reliability of NIRS models, paving the way for more stable and accurate real-world applications.
More information: Zhuopin Xu et al, Method for screening near-infrared quantitative models with high robustness, Analytica Chimica Acta (2025).
Journal information: Analytica Chimica Acta
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences