Novel drug-loading technique: Cubosome-based method incorporates mRNA into exosomes in 10 minutes

Sadie Harley
scientific editor

Robert Egan
associate editor

Exosomes, naturally derived vesicles responsible for intercellular communication, are emerging as next-generation drug delivery systems capable of transporting therapeutics to specific cells. However, their tightly packed, cholesterol-rich membranes make it extremely difficult to encapsulate large molecules such as mRNA or proteins.
Conventional approaches have relied on techniques like electroporation or chemical treatment, which often damage both the drugs and exosomes, reduce delivery efficiency, and require complex purification steps—all of which pose significant barriers to commercialization.
A joint research team led by Dr. Hojun Kim at the Center for Advanced Biomolecular Recognition and Dr. Hong Nam Kim at the Center for Brain Convergence Research of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) has developed a novel drug-loading technique that allows large biomolecules to be efficiently incorporated into exosomes simply by mixing.
The study is in the journal Nature Communications.
This breakthrough enables stable drug encapsulation in under 10 minutes, eliminating the need for specialized equipment or complex processing.
The team utilized a lipid-based nanoparticle known as a "cubosome," which mimics the fusion structure of cell membranes and naturally fuses with exosomes.
By mixing cubosomes carrying mRNA with exosomes at room temperature for just 10 minutes, the researchers achieved efficient fusion and confirmed that the mRNA was successfully loaded into the exosomes. Analysis showed that over 98% of the mRNA was encapsulated, while the structural integrity and biological function of the exosomes were preserved.
-

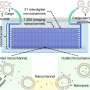
A conceptual diagram illustrating how cubosomes and exosomes merge via membrane fusion, enabling the transfer of large biomolecular drugs—such as mRNA and proteins—into the exosome interior. Experimental results confirmed the successful high-efficiency loading of various macromolecular therapeutics. Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) -

Hybrid exosomes loaded with drugs were shown to effectively cross the blood-brain barrier and deliver therapeutic molecules into brain tissue. These findings demonstrate the platform's strong potential as a precision-targeted treatment for neurological disorders. Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST)
Furthermore, the engineered exosomes demonstrated the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, one of the most difficult hurdles in drug delivery. Notably, the team observed a "homing" effect, where exosomes return to the type of cell they originated from, enabling targeted drug delivery to diseased tissues.
This technology achieves efficient loading of large biomolecules without altering the exosomes themselves, opening the door to practical applications of exosome-based therapies in precision medicine.
The technique is highly adaptable to clinical environments, as it requires no specialized equipment or complex processing. It preserves exosome function while enabling the delivery of large payloads, offering broad potential for the treatment of intractable diseases, including neurological disorders, cancer, and autoimmune conditions.
The team plans to conduct further safety evaluations for clinical translation and establish a mass production system for cubosomes.
Dr. Hojun Kim of KIST stated, "This technology allows medical professionals to easily combine exosomes and therapeutic molecules at the clinical site, making it a meaningful step toward realizing personalized medicine."
Dr. Hong Nam Kim added, "Because it enables precise drug delivery even in complex tissues such as the brain, it holds great potential for treating a wide range of diseases."
More information: Gamsong Son et al, Fusogenic lipid nanoparticles for rapid delivery of large therapeutic molecules to exosomes, Nature Communications (2025).
Journal information: Nature Communications