Research redefines the properties of faults when rock melts
Geoscientists at the University of Liverpool have used friction experiments to investigate the processes of fault slip.

Geoscientists at the University of Liverpool have used friction experiments to investigate the processes of fault slip.

Professors Frederick Gosselin and Daniel Therriault, along with their master's student Renaud Passieux, are not related to Spiderman. Nevertheless, these Polytechnique Montreal researchers have produced an ultra-tough polymer ...

Microalgae offer a highly promising alternative to petroleum products without competing for resources used in the food industry. They have now been used for the first time to make asphalt. Researchers have recently proved ...

Researchers of the Universitat Politècnica de València and the Instituto de AgroquÃmica y TecnologÃa de Alimentos (IATA) of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) have obtained in the laboratory a new yogurt with ...
When it comes to boiling water—or the phenomenon of applying heat to a liquid until it transitions to a gas—is there anything left for today's scientists to study? The surprising answer is, yes, quite a bit. How the bubbles ...

Just because concrete is the most widely used building material in human history doesn't mean it can't be improved. A recent study conducted by researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the ...
Windows allow brilliant natural light to stream into homes and buildings. Along with light comes heat that, in warm weather, we often counter with energy-consuming air conditioning. Now scientists are developing a new kind ...

From a mechanical perspective, granular materials are stuck between a rock and a fluid place, with behavior resembling neither a solid nor a liquid. Think of sand through an hourglass: As grains funnel through, they appear ...
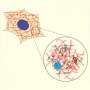
Conventional wisdom holds that the cytoplasm of mammalian cells is a viscous fluid, with organelles and proteins suspended within it, jiggling against one another and drifting at random. However, a new biophysical study led ...

Estonian-born Katerina Alba's research at the University of Huddersfield could help to improve the quality of some of the most popular emulsion-based food products – such as butter, mayonnaise, yoghurt and fruit drinks ...