Sulfur molecules from space may have seeded early life on Earth
Important nutrients for the first living organisms on Earth may have come from space, according to new research from the University of Hawai驶i at M膩noa.
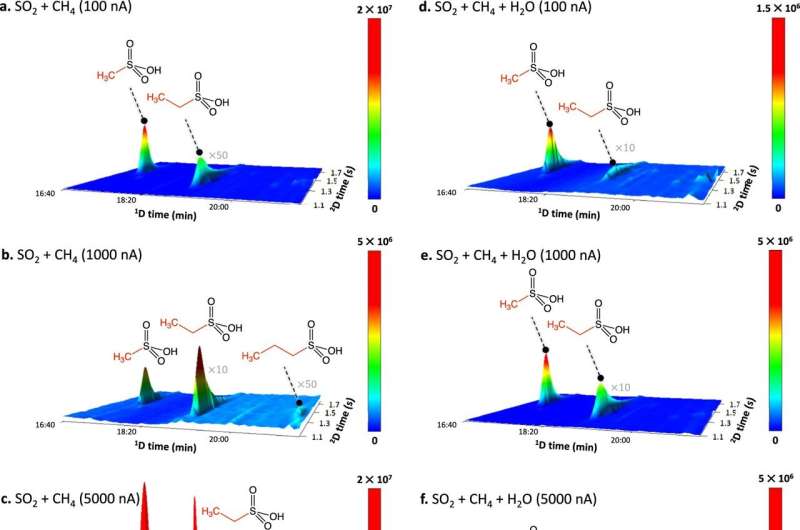
Department of Chemistry scientists discovered that certain sulfur-containing organic molecules, called alkylsulfonic acids, can form naturally in space without the presence of life and were delivered to Earth by comets and asteroids.
Sulfur-containing organic molecules are essential for life on Earth as they are crucial for many biological processes, such as protein structure and function, enzyme activity, and cellular respiration to incorporate sulfur.
These organic molecules were created in laboratory simulations that mimic the conditions of interstellar ices found in space. The study also discusses how this discovery could help scientists detect these molecules on comets and asteroids, such as the carbonaceous asteroid Ryugu, providing insights into the chemical processes that might contribute to the origins of life on Earth.
The work is in the journal Nature Communications.
"Our discovery highlights the creativity and persistence of scientists in solving long-standing mysteries about life's beginnings, inspiring curiosity and interest in scientific exploration and research," said UH M膩noa Professor Ralf I. Kaiser who is one of the study's authors. "Understanding this process can ignite imaginations about our place in the universe and the origins of life itself."
"Life as we know it requires sulfur, and ancient water-soluble alkylsulfonic acids are a plausible way to incorporate sulfur into early organisms," added Mason McAnally, a UH M膩noa chemistry Ph.D. student and lead author.
More information: Mason McAnally et al, Abiotic formation of alkylsulfonic acids in interstellar analog ices and implications for their detection on Ryugu, Nature Communications (2024).
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by University of Hawaii at Manoa